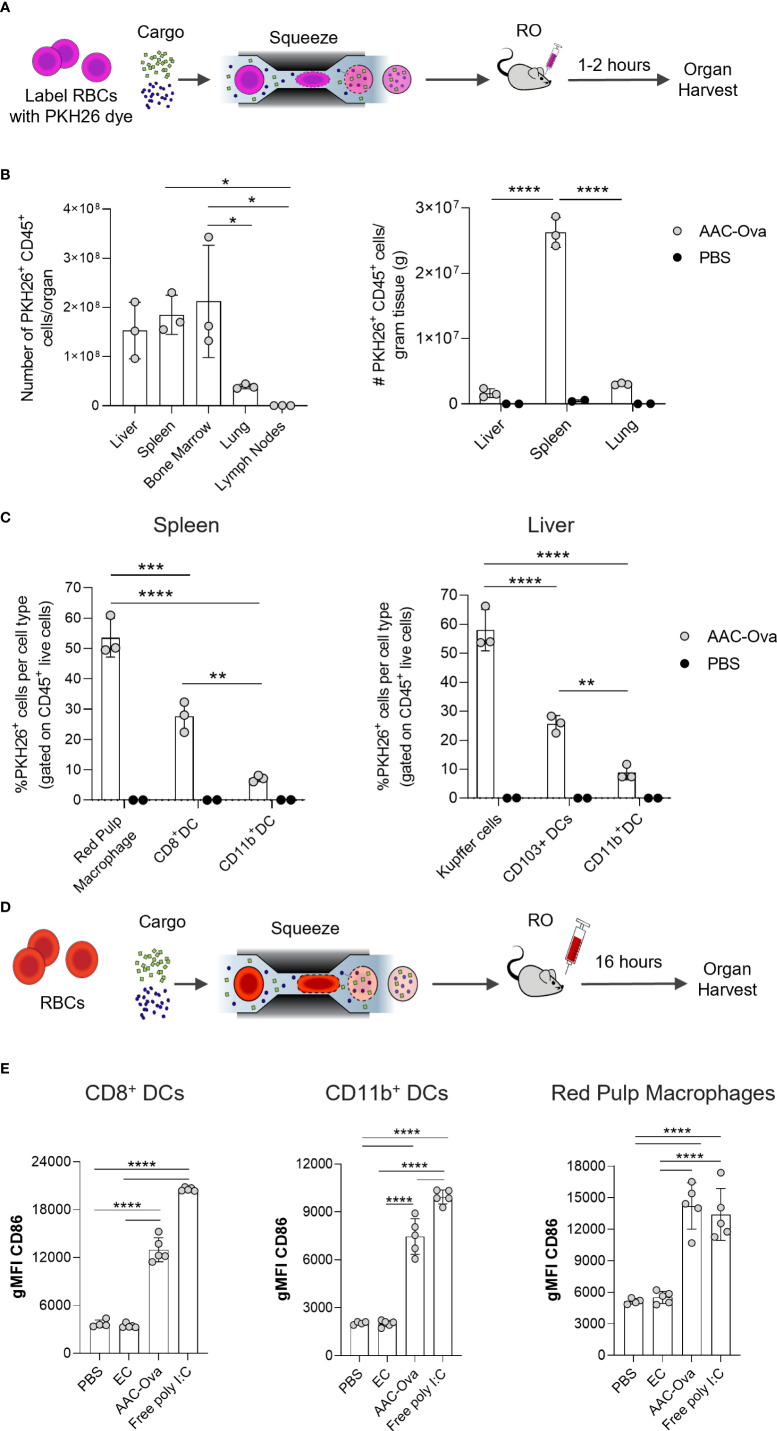
Figure 3.
Mouse AACs are rapidly internalized by APCs, inducing maturation in vivo. Murine RBCs were squeezed in the presence of Ovalbumin (Ova) and poly I:C to generate AAC-Ova and injected RO at 1x109 per animal. AAC uptake studies (A–C) used PKH26-labeled RBCs and organ analysis was performed 1–2 hours after PKH26-labeled AAC-Ova injection. (B) The number of PKH26+ CD45+ cells was determined for each organ. Liver, spleen, and lung were weighed to determine PKH26+ CD45+ cells per gram tissue for animals injected with AAC-Ova (n = 3 mice) or PBS (n = 2 mice). (C) The cell type for PKH26-AAC-Ova uptake was determined in the spleen and liver. For APC maturation studies (D, E), unlabeled RBCs were used for squeeze and organs analyzed the day following AAC-Ova administration. (E) Upregulation of CD86 maturation marker on recipient mouse splenic APCs following uptake of AAC-Ova. Figures show one dot per mouse for all studies. n = 2 independent uptake studies, and n = 3 independent maturation studies. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P ≤ 0.0005, ****P < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA.