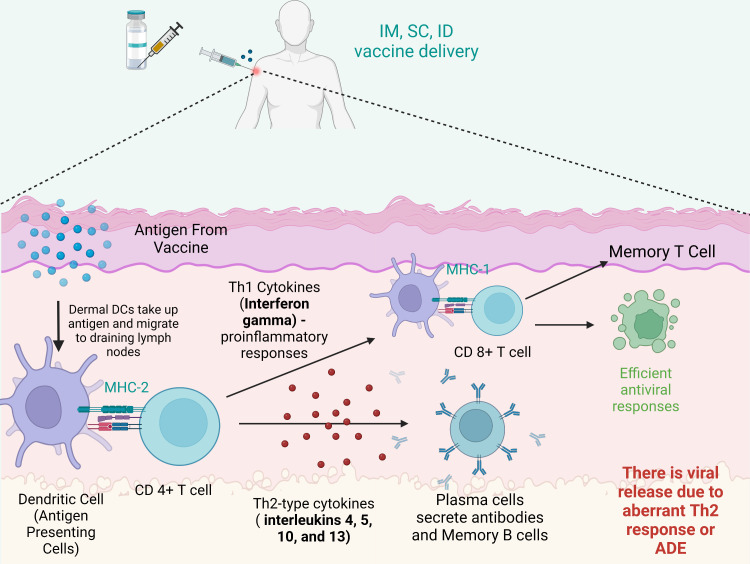
Figure 5.
Immune reaction after vaccination. After intramuscular (IM), intradermal (ID) or subcutaneous (SC) vaccine delivery, dermal dendritic cells (DCs) take up antigens and migrate to draining lymph nodes to stimulate T cells (CD8+ T cells and CD4+ T cells). Plasma cells secrete antibodies and memory B cells. CD8+ T cells can be stimulated by Th1 cytokines and in turn acquire the ability to attack the infected cells. However, imbalanced immune responses have the potential to cause pulmonary immunopathology, partially due to an aberrant Th2 response or antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE). Created with BioRender.com.