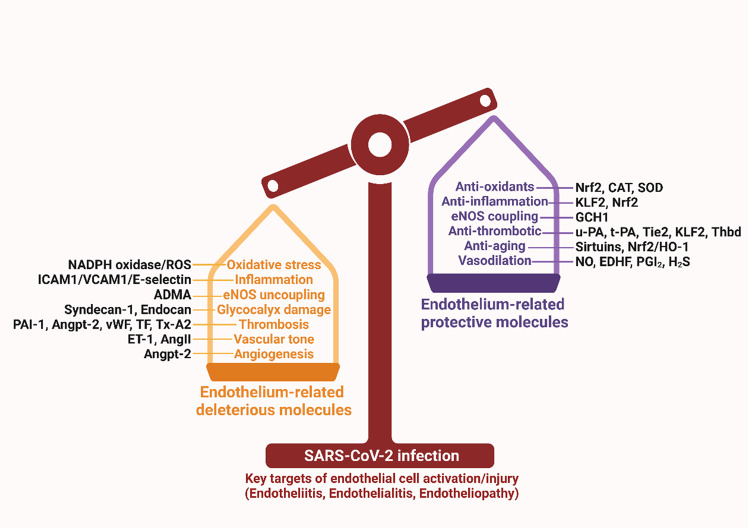
Fig. 1. SARS-CoV-2 induced endothelial dysfunction.
SARS-CoV-2 infection alters the balance of endothelial protective molecules and endothelial damaging molecules, leading to endothelial dysfunction. ADMA asymmetrical dimethylarginine, AngII angiotensin II, Angpt-2 angiopoietin-2, CAT catalase, EDHF endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor, eNOS endothelial nitric oxide synthase, ET-1 endothelin 1, GCH1 GTP cyclohydrolase 1, H2S hydrogen sulfide, HO-1 heme oxygenase-1, ICAM1 intercellular adhesion molecule 1, KLF2 krüppel-like factor 2, NO nitric oxide, Nrf2 nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2, PAI-1 plasminogen activator inhibitor 1, PGI2 prostaglandin I2, ROS reactive oxygen species, SOD superoxide dismutase, TF tissue factor, Thbd thrombomodulin, Tie-2 tyrosine-protein kinase receptor, tPA tissue plasminogen activator, Tx-A2 thromboxane A2, uPA urokinase plasminogen activator, VCAM1 vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, vWF von Willebrand factor.