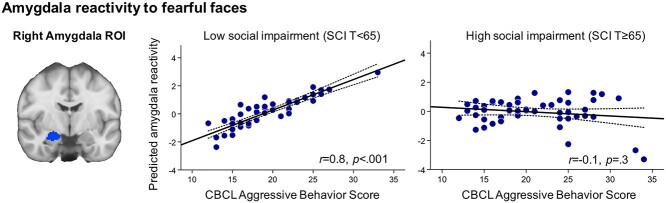
Figure 3.
Amygdala reactivity to fearful faces is associated with severity of aggressive behavior in youth. In the aggressive behavior group (n = 101), results of regression analyses revealed a significant CBCL Aggressive Behavior × SRS-2 SCI interaction for right amygdala reactivity to fearful versus calm faces. That is, right amygdala reactivity to fearful faces was associated with severity of aggressive behavior for children with aggression without social deficits (β = −1.1, t = −2.1, P = 0.04) but not for children with aggression with social deficits (P > 0.1) after controlling for age, IQ, and CU traits. The x-axis shows CBCL Aggressive Behavior Scale scores, which was used as a continuous measure of severity of aggression. The y-axis shows residualized amygdala reactivity with age, IQ, and CU traits partialled out. The left panel shows the right amygdala region-of-interest, which was structurally defined using the Harvard-Oxford atlas in FSL. For visualization, scatterplots display a median split using a T-score of 65 on the SRS-2 SCI subscale.