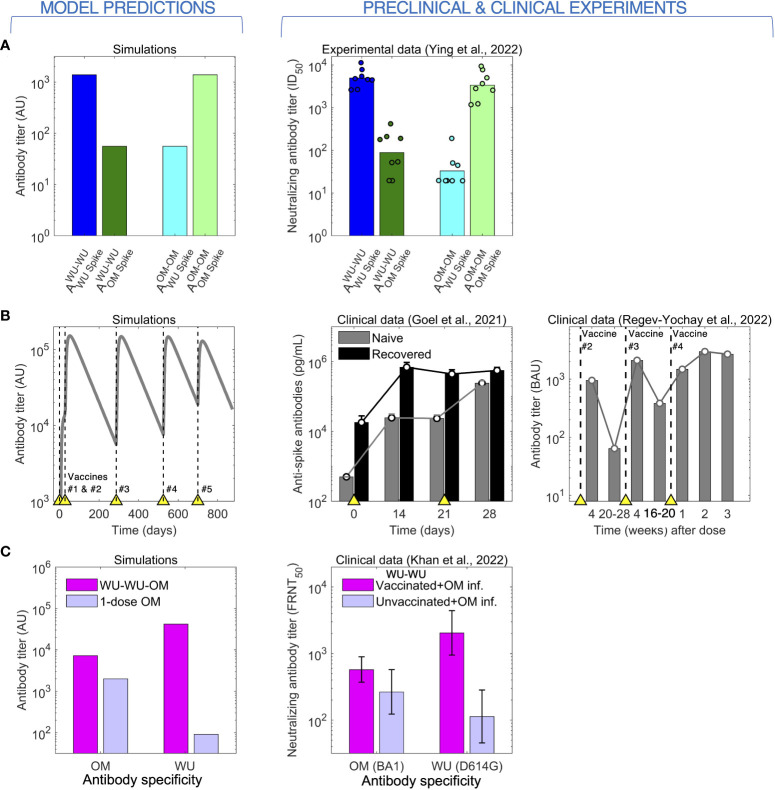
Figure 2.
The model predicts (left) antibody responses to CoV-2 following vaccination and infection (right). (A) Immunization of mice with 2 doses of either the WU- or the OM-vaccine. High antibody titers to a given antigen (WU or OM) requires 2 vaccinations with that antigen. (B) Antibody titers saturate following repeated immunization or infection. Left panel: Simulations of repeated immunizations with the WU-vaccine at times indicated by the yellow triangles. The antibody response to the WU-virus increases substantially after the first two vaccinations. Further boosts with the same vaccine results in little further increases in the titer of antibody. Center panel: data for the virus titer in naive (grey) and CoV-2 infected and recovered (black) individuals following two doses of the WU-vaccine. The titer of antibodies in recovered individuals saturates after a single vaccination, while that in naive individuals is boosted by the second vaccination. Right panel: antibody titers following four doses of the WU-vaccine shows plateauing after vaccination #3. (C) Two stimulations with the WU-antigen enhance the subsequent responses to OM (following OM stimulation).