FIGURE 2.
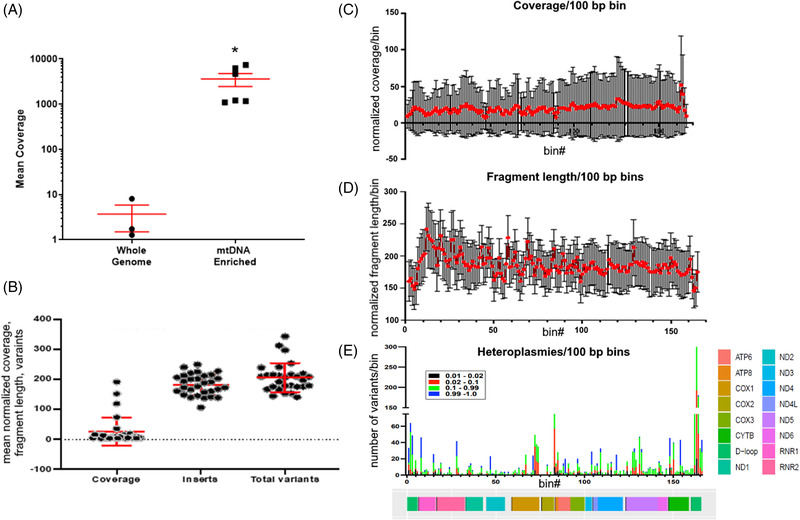
Enrichment, mean genome‐wide coverage, fragment length and total variants in trauma patients. (A) Target‐bait capture enrichment in combination with the judicious exclusion of nuclear mitochondrial (NUMT) leads to significant enrichment of the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) genome versus whole genome sequencing of cell‐free plasma. Enrichment efficiency was calculated for mean coverage of the mtDNA genome (reads/base) after whole genome sequencing and after target‐bait enrichment in four individual patients. Mean ± standard error of the mean; *p ≤ .05. (B) Normalized mean coverage of mtDNA (mean coverage/mean NUMT coverage), fragment length (mean length, measured in bp) and a number of heteroplasmies for all 30 trauma patients. Hundred base pair nonoverlapping bins of (C). normalized mean coverage across the mtDNA genome and (D) mean fragment length across the ≈16.5 kb expanse of the mitochondrial genome. (E) Heteroplasmic variants in all 30 patients as reported in 100 bp bins, where colour demarcates the variant allele fraction (VAF) of the variants. See “methods” for details.
