Figure 3.
Delivery of LV to mouse kidney by retrograde ureter injection
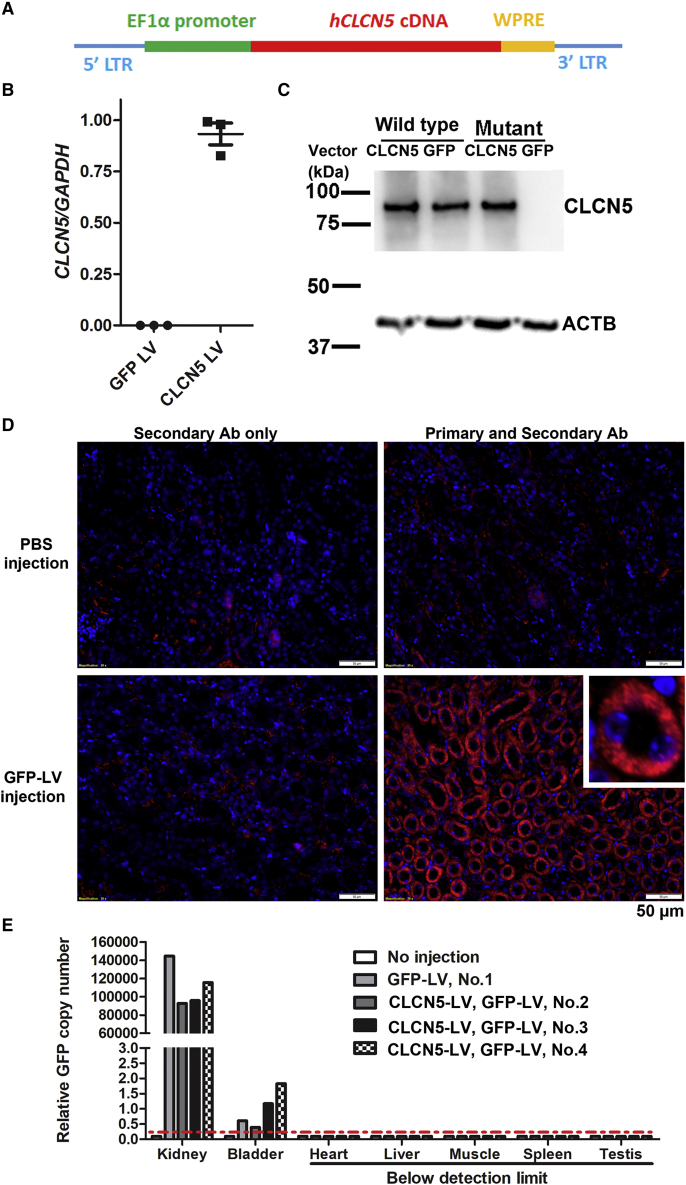
(A) Components of the human ClC-5-expressing LV. Human CLCN5 cDNA was codon optimized to distinguish the transgene with the endogenous human cDNA. LTR, long terminal repeats. (B) LV-mediated CLCN5 mRNA expression in HEK293T cells. ClC-5- and GFP-expressing LVs (10 ng p24) were transduced into 2.5 × 104 HEK293T cells. Forty-eight hours after transduction, CLCN5 expression was detected by qRT-PCR with primers specific for the codon-optimized human CLCN5 mRNA (hCLCN5-F and hCLCN5-R; see Table S14 for sequences). (C) Western blots for ClC-5 protein in transduced kidney proximal tubule cells. ClC-5-expressing LVs (28 ng p24) were transduced into 2.5 × 105 kidney proximal tubule cells isolated from wild-type and mutant mice. Confirmatory western blotting was performed 72 h after transduction. (D) GFP protein expression in mouse kidney 2 weeks after GFP LV delivery by retrograde ureter injection. The 6-month-old, wild-type mouse received GFP LV injection in both kidneys. GFP expression was detected by immunofluorescence (shown in red). Inset: enlarged view of a GFP-positive tubule. Nuclei were stained by 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (shown in blue). (E) GFP LV DNA in the organs shown, as detected by qPCR 2 weeks after GFP LV delivery. Genomic DNA samples isolated from different organs were used as templates in qPCR to detect GFP DNA. Mouse no. 1 was the same mouse shown in (D). Mice nos. 2, 3, and 4 were male Clcn5 mutant mice that received GFP LV injection 10 months following CLCN5 LV injection. All mice were euthanized 2 weeks after GFP LV injection. The red dashed line indicates detection limit.