Figure 4. Dual laser treatment decreased the expression of PD-1 on tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes (TILs).
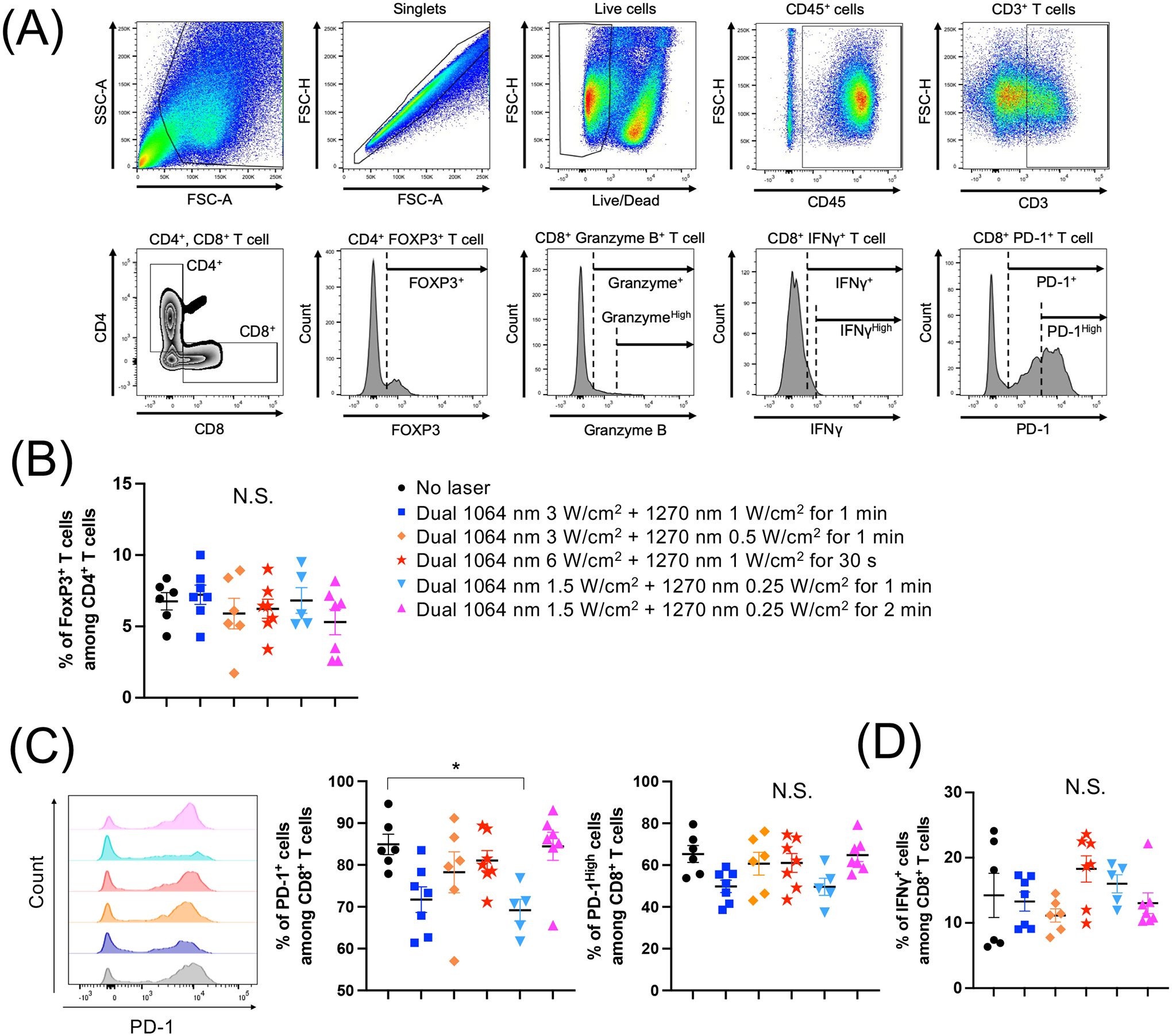
E0771 murine breast cells were injected into the flank of C57BL/6J mice. The tumors were then treated by various combinations of 1064 nm (1.5–3 W/cm2) and 1270 nm (0.25–1 W/cm2) laser for 30–120 s for 5 consecutive days, from day 3 to 7. On day 16, tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes (TILs) were purified from tumors. Single-cell suspensions of TILs were stained for surface markers and cytokines, and then analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) Gating strategy. (B) Percentages of FOXP3+ CD4+ T cells. (C) Representative histograms and percentages of programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and (D) IFN-γ expression in CD8+ T cells are shown. (A-D) n= 6, 7, 6, 7, 5, 7 for no laser, 1064 nm 3 W/cm2 + 1270 nm 1 W/cm2 for 1 min, 1064 nm 3 W/cm2 + 1270 nm 0.5 W/cm2 for 1 min, 1064 nm 6 W/cm2 + 1270 nm 1 W/cm2 for 30 s, 1064 nm 1.5 W/cm2 + 1270 nm 0.25 W/cm2 for 1 min, 1064 nm 1.5 W/cm2 + 1270 nm 0.25 W/cm2 for 2 min, respectively. *P < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test.
