Fig. 4. Opposing effect of ELB00824 on oxaliplatin-induced hyperexcitability in IB4− and IB4+ DRG neurons.
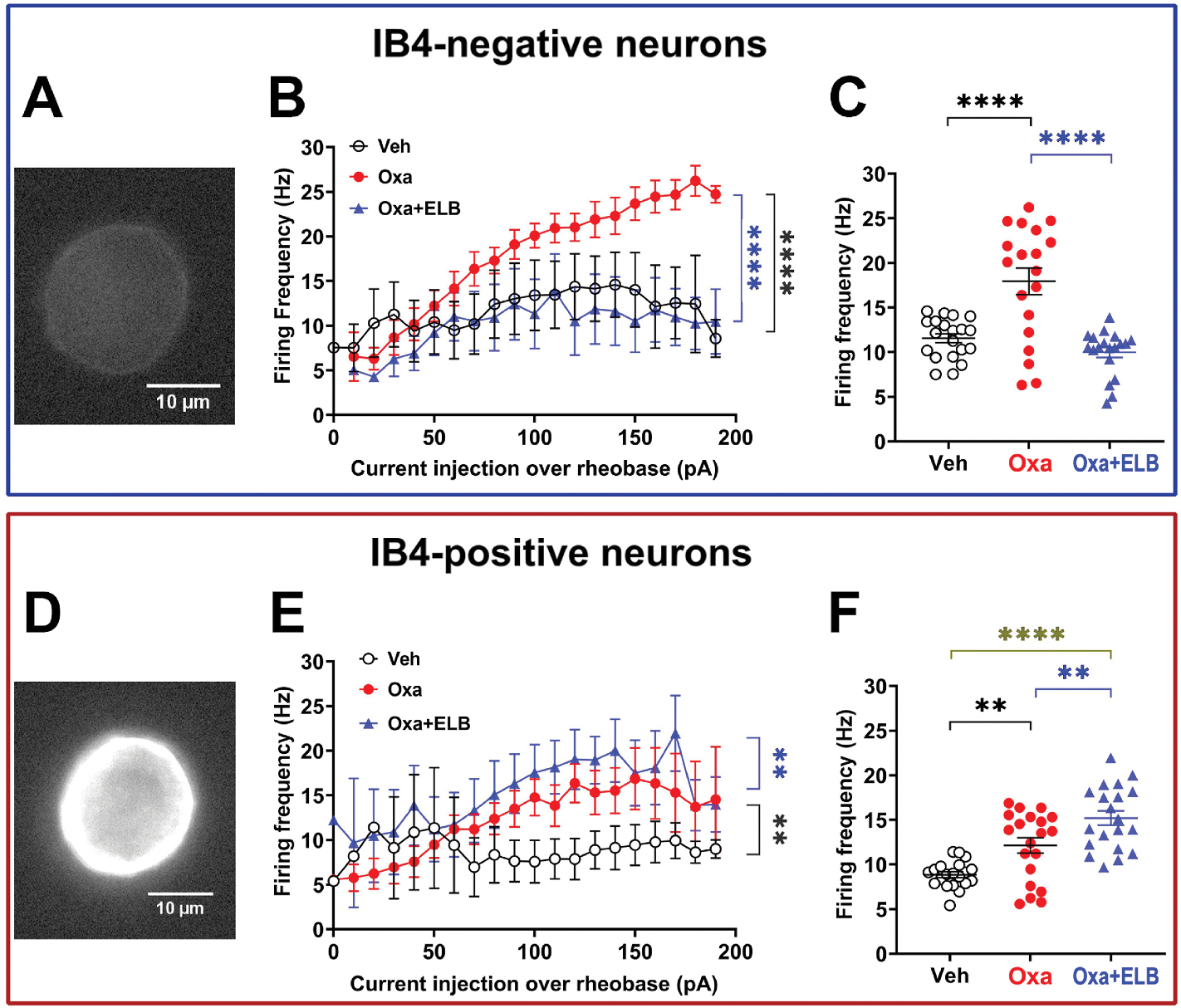
Oxaliplatin-induced hyperexcitability was characterized in vitro in IB4− (A-C) or IB4+ (D-F) DRG neurons. (A and D) Examples of Alexa-488-conjugated IB4 immunoreactivity in IB4− (A) or IB4+ (D) neurons. (B and E) Firing frequency as a function of the injected current in the range of 0–200 pA in 10-pA pulses for IB4− (B) or IB4+ (E) neurons exposed to the following 3 different treatment. (C and F) Firing frequencies from figures B and E, respectively, were plotted as a function of the following 3 treatment groups. Veh: vehicle, Oxa: oxaliplatin 1 h pre-treatment in vitro. Oxa + ELB: Oxaliplatin pre-treatment + 10 μM ELB0024 combined pre-treatment for 1 h in vitro. Number of neurons from 6 naïve male mice were as follows: Veh, n = 8 (B-C) or 7 (E-F); Oxa, n = 5 (B-C) or 9 (E-F), Oxa + ELB, n = 5 (B-C) or 7 (E-F). Comparison of data from plot. Symbols at mean and error bars at standard error of the mean (SEM) were plot. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.0001, ****p < 0.0001, ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. In figure D and G, pairwise comparison between Oxa group and Oxa + ELB group is indicated with blue line, and that between Oxa group and Veh group is indicated with black line. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
