Fig. 5. ELB00824 reduces oxaliplatin-induced oxidative stress in HEK cells and in the spinal cord.
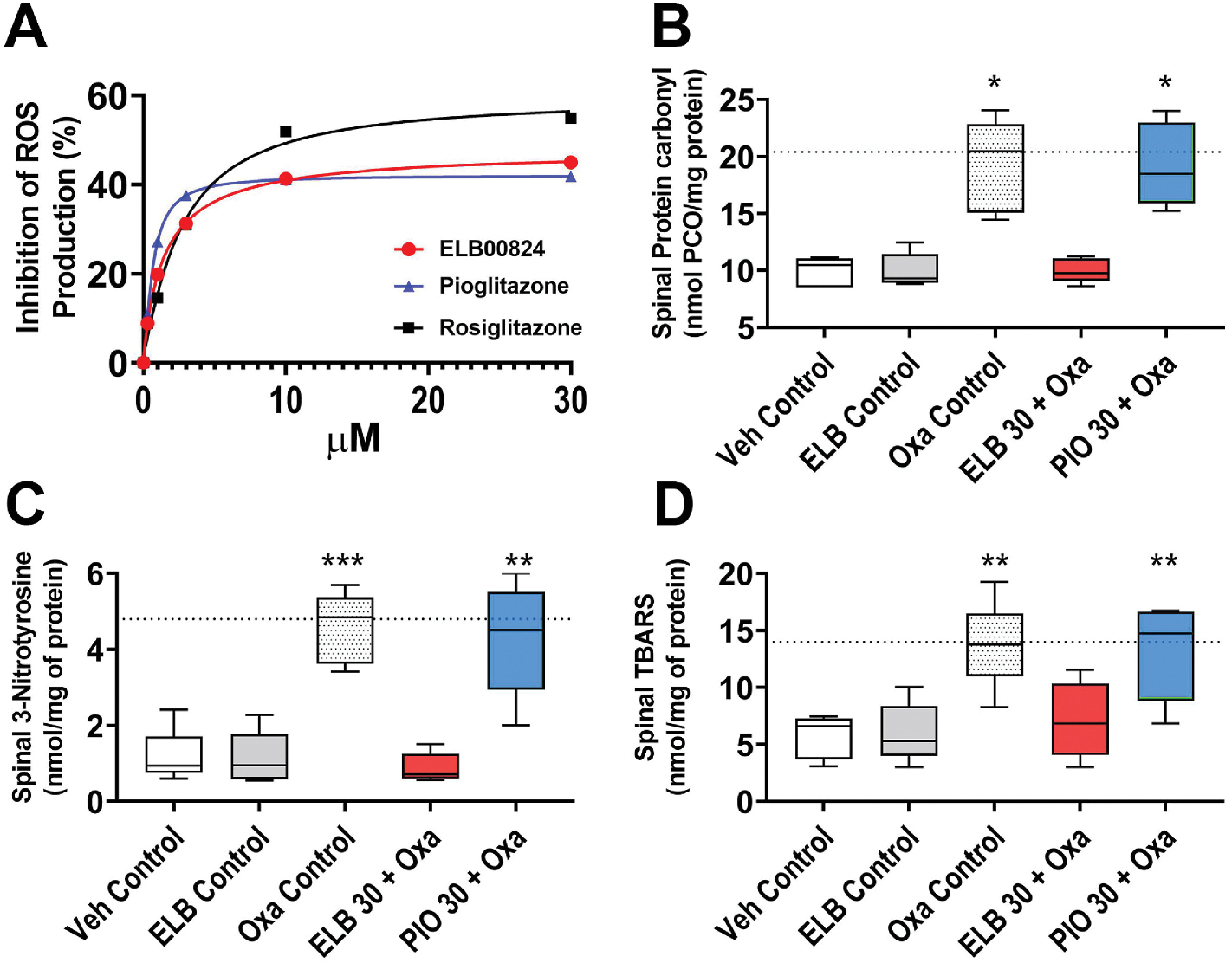
(A)The anti-oxidative effect of ELB00824 was identified in vitro, where PPARγ agonists (ELB00824, rosiglitazone, pioglitazone), concentration dependently inhibit ROS production in HEK 293 T cell lines. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments with similar results, normalized to control response in each case (mean ± SD), and fitted using a sigmoidal dose–response curve (Sigmoidal, Sigmoid, 4 Parameter). (B-D) The CNS specific anti-oxidative effect was further confirmed with lumbar spinal cords dissected out from the mouse treatment groups at the end of oxaliplatin treatment period. ELB00824 normalizes oxaliplatin-induced increase in spinal oxidative stress indicated by the levels of the byproducts of protein oxidation (carbonyl level in B, 3-Nitrotyrosine level in C), and lipid peroxidation [Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) level in D]. The box-and-whiskers plots (B-D) show minimum, maximum, median and 25th and 75th percentiles. Inter-group comparison used one-way ANOVA, followed by Dunn’s test. *: p ≤ 0.05; **: p ≤ 0.01; ***: p ≤ 0.001 vs Veh Control group. Dashed line is the mean value of Oxa control group at the end of oxaliplatin treatment period in chronic OIPN model.
