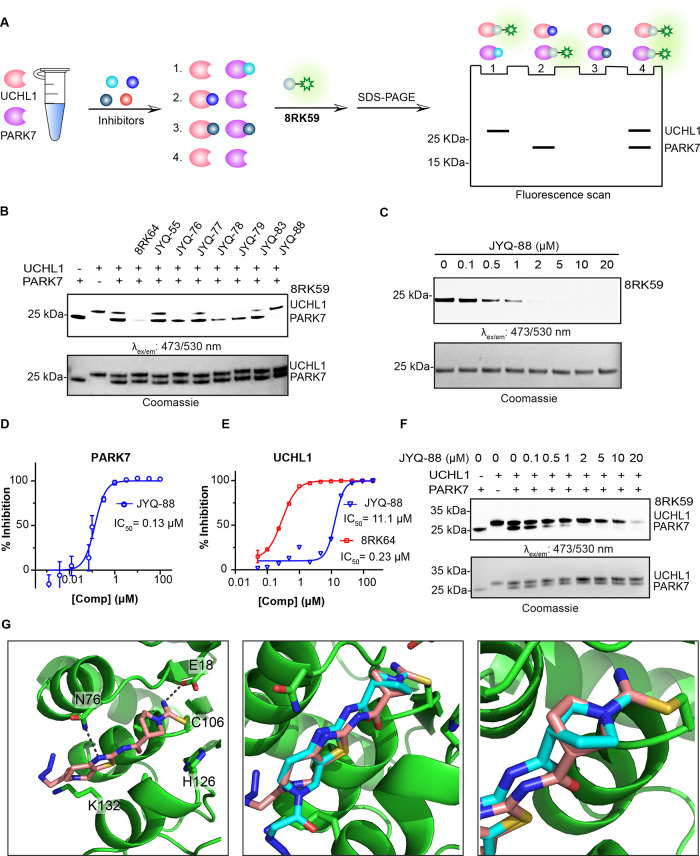
Figure 3.
Selectivity analysis of the inhibitors and structural characterization of JYQ-88 binding to PARK7. (A) Schematic representation of the gel-based competition assay to identify selective PARK7 inhibitors. (B) Activity and selectivity evaluation of PARK7 inhibitors. PARK7 and UCHL1 (1 μM) were incubated with indicated compounds (2 μM), followed by incubation with 8RK59. (C) Activity evaluation of JYQ-88 for PARK7. PARK7 (1 μM) was incubated with increasing concentrations of JYQ-88, followed by incubation with 8RK59. (D) IC50 determination of JYQ-88 for PARK7 by the DiFMUAc assay. (E) IC50 determination of JYQ-88 and 8RK64 for UCHL1. (F) Selectivity determination of inhibitor JYQ-88 between UCHL1 and PARK7. PARK7 and UCHL1 were incubated with a serial dilution of JYQ-88, followed by incubation with 8RK59. (G) Co-crystal structure of the PARK7–JYQ-88 complex (PDB:7PA3). PARK7 in green, JYQ-88 in pink, and 8RK64 in cyan. Overlay between 8RK64 and JYQ-88 is shown in the middle panel with a zoom-in shown on the right. The cyanopyrrolidine moiety has rotated 180°.