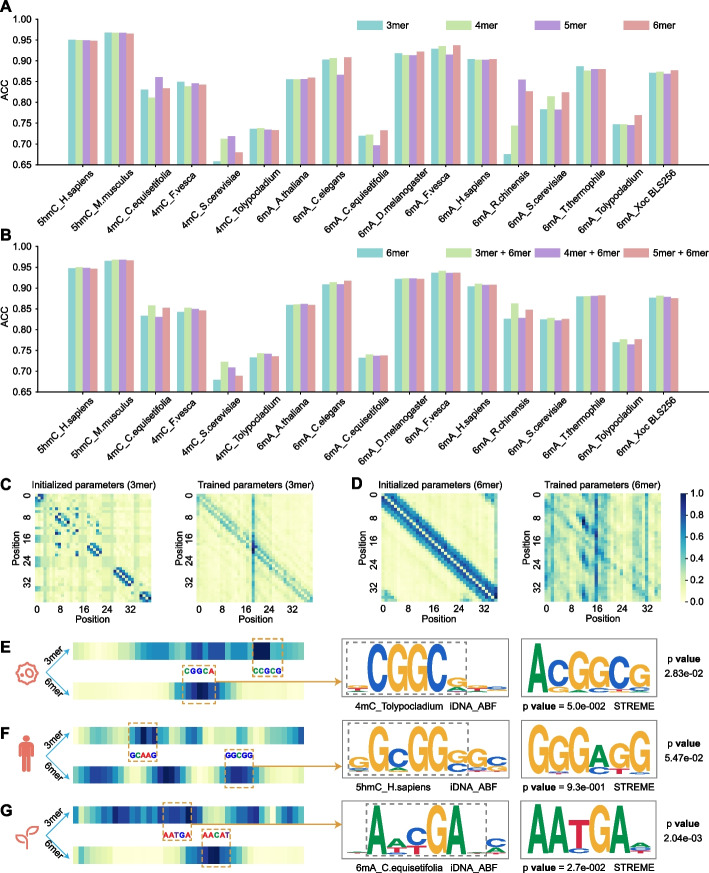
Fig. 3.
Interpretable analysis of multi-scale information processing. A The comparison of single scales including 3-mer, 4-mer, 5-mer, and 6-mer, respectively. B The comparison of multi-scale combinations. C The attention map to illustrate the information captured at 3-mer scale on one randomly selected sequence. Two sub-figures visualize the change of information captured before and after training, respectively. D The attention map to illustrate the information captured at 6-mer scale. E–G Interpretable illustrations of the motifs learnt by our model in three species covering three methylation types, including 4mC_Tolypocladium, 5hmC_H.sapiens, and 6mA_C.equisetifolia, respectively. The left part figure clearly shows which region the model is more focused on by using heatmap from 0 to 1. The closer the score is to 1, the darker the color and the more important the region considered by the model. The p-value was calculated using TOMTOM by comparing our iDNA-ABF learnt motifs with STREME motifs. The p-value in STREME was calculated by a one-sided binomial test. The motifs within the gray dashed anchor boxes were extracted for pair comparisons