Exhibit 2:
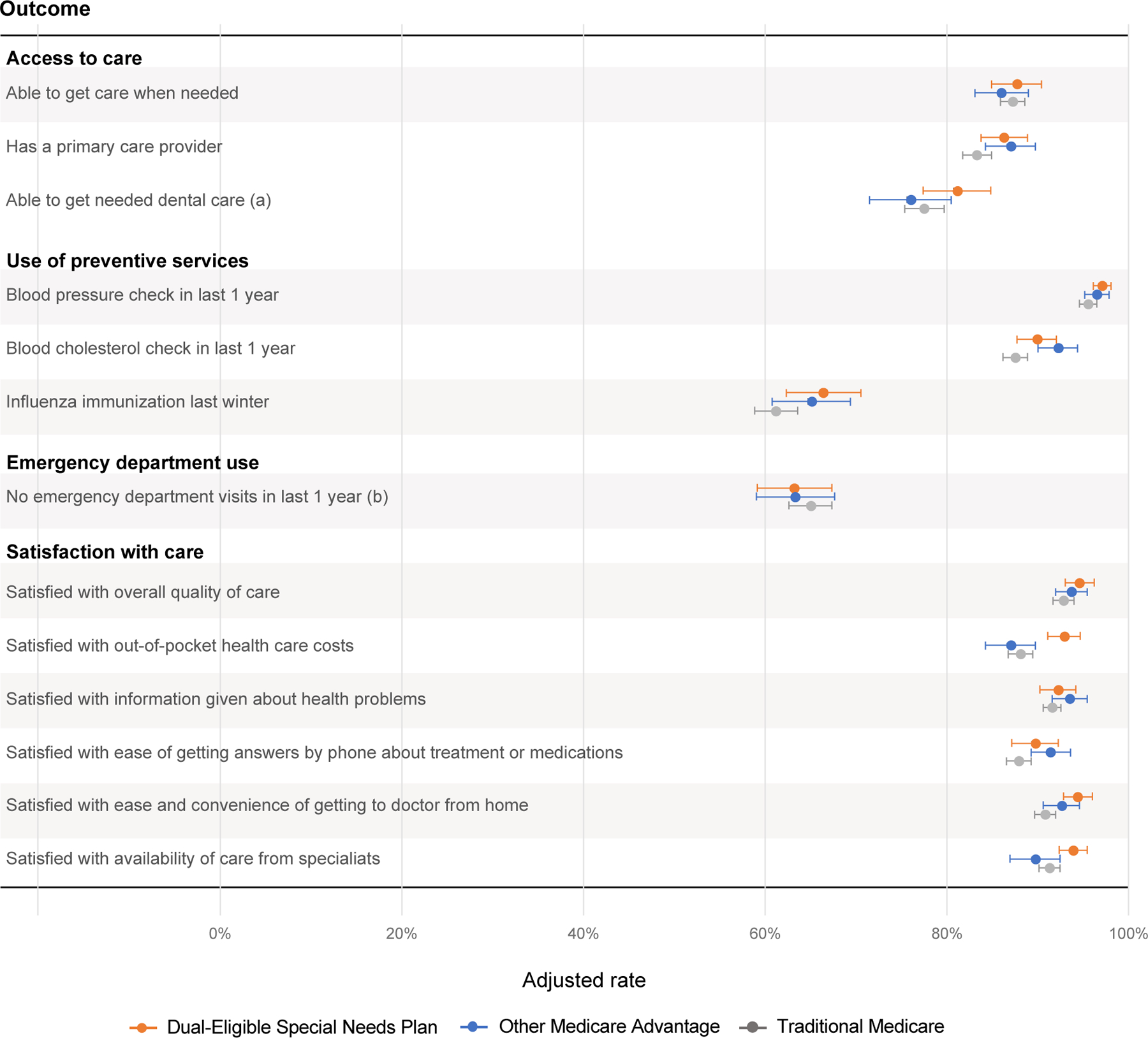
Access to, use of, and satisfaction with care among dual-eligibles enrolled in Dual Eligible Special Needs Plans, other Medicare Advantage plans, and traditional Medicare
Notes: Figure displays adjusted rates of study outcomes among dual eligibles in Dual Eligible Special Needs Plans (D-SNPs), other Medicare Advantage plans not exclusively serving dual eligibles, and traditional Medicare. Shaded circles show adjusted estimates. Error bars show 95% confidence intervals, constructed using robust standard errors clustered at the respondent level to account intra-person correlation over time. Estimates adjusted for covariates in Exhibit 1, annual supply of physicians per 1,000 county residents, annual supply of dentists per 1,000 county residents, state fixed effects, and year fixed effects, and weighted by a composite of propensity score weights and survey weights. Adjusted estimates calculated using the method of average marginal effects (see Appendix for details). Exhibit 3 reports corresponding regression estimates for the adjusted differences in study outcomes between dual eligibles enrolled in D-SNPs vs. other Medicare Advantage plans or traditional Medicare.
a Question not asked in the 2015 MCBS.
b Question was asked only of new survey respondents in the 2015 and 2016 MCBS.
Source: Authors’ analyses of the MCBS from 2015–2019.
