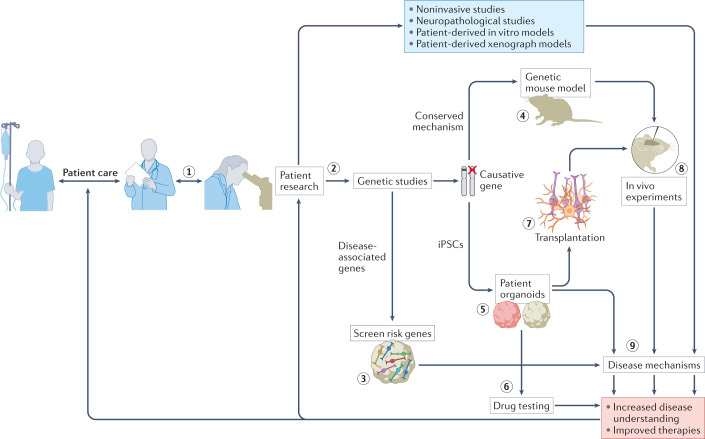
Fig. 5. The role of brain organoids in neurological research.
Close collaboration with medical specialists is required to increase the accuracy of organoid models (step 1). Patient research is the foundation for developing organoid models (step 2). Identification of disease-associated genes enables these genes to be screened in organoids to inform disease risk and provide insights into disease mechanisms (step 3). Identification of causative genes enables development of accurate screening platforms. When these genetic mechanisms are conserved in rodents, genetic mouse models can be developed to perform in vivo experiments (step 4). However, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from patients can also be used to establish patient-derived organoids (step 5). These models can be used for drug testing (step 6) that leads to improved therapies. Cells from these organoid models can also be transplanted (step 7) into animals for in vivo evaluation of human cell types (step 8). All of these organoid-based models can provide insights into disease mechanisms (step 9). The increased understanding of disease and improvements in therapies that result feed back into patient care and patient research.