Extended Data Figure 8: Decoding performance for relative and absolute social rank, and competitive success with different datasets.
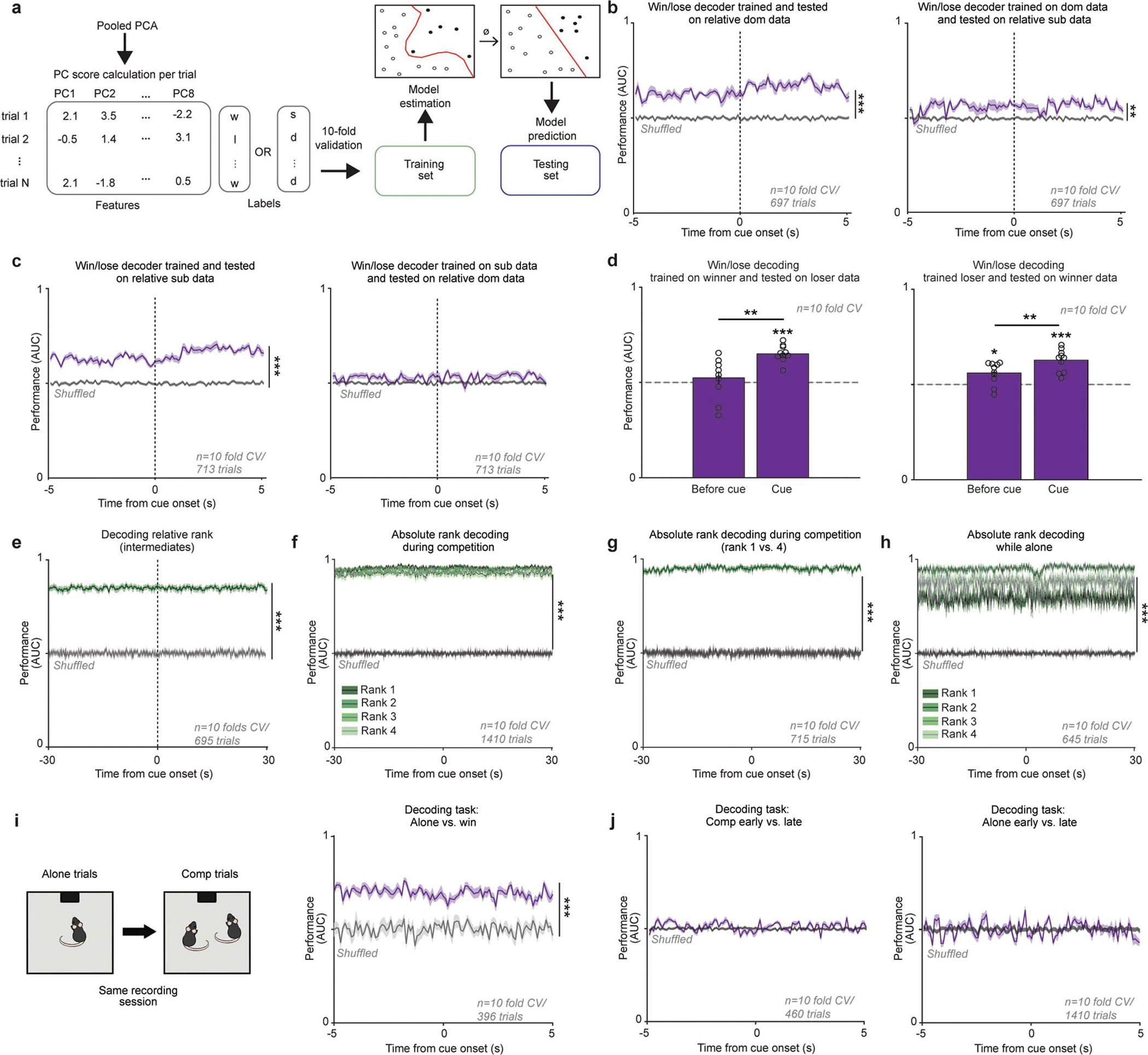
a, Support Vector Machine (SVM) data pipeline to decode rank or competition outcome based on single trial population mPFC data in the common behavioral subspace. b, mPFC population encoding of win/lose in relative dominants generalizes to relative subordinates. Decoding performance (area under the receiving operating curve; AUC) when (left) training and testing on relative dominant data or (right) training on dominant and tested on relative subordinate data was higher than chance (shuffled performance indicated in gray). (Wilcoxon rank sum, dom/dom p=0.0002, dom/sub p=0.003). c, mPFC population encoding of win/lose in relative subordinates does not generalize to relative dominants. Decoding performance (area under the receiving operating curve; AUC) when (left) training and testing on relative subordinate data was higher than chance but not when (right) testing on relative dominant data (shuffled performance indicated in gray). (Wilcoxon rank sum, sub/sub p=0.0002, sub/dom p=0.14). d, Decoder performance for classifying competition outcome using training data from winner data (e.g. mouse won majority of trials) and testing data from loser data (e.g. mouse lost majority of trials) and using training data from loser data and testing data from winner data (Wilcoxon rank sum: left, baseline vs shuffle p=0.10, left, cue vs shuffle p=0.0002, right, baseline vs shuffle p=0.02, right, cue vs shuffle p=0.0002; Wilcoxon sign rank: loser base vs cue p=0.002, winner base vs cue p=0.004). All error bars indicate standard error from 10-fold cross-validation. e, SVM performance for decoding relative rank specifically for intermediate (ranks 2 or 3) mice; mean AUC vs shuffled AUC Wilcoxon rank sum: p=0.0002). f, Absolute rank can be decoded from mPFC population activity during social competition. One model was trained per absolute rank (mean performance across ranks vs shuffled data; Wilcoxon rank sum p=0.0002). g, Absolute rank can be decoded for rank 1 and 4 animals from mPFC population activity during social competition. One model was trained to discriminate rank 1 trials from rank 4 (mean performance across ranks vs shuffled data: Wilcoxon rank sum p=0.0002). h, Absolute rank can be decoded from mPFC population activity in mice performing reward task alone. One model was trained per absolute rank (mean performance across ranks vs shuffled data; Wilcoxon rank sum p=0.0002). i, Left, experimental design. In 15 mice the same neurons were recorded during alone trials and followed by competition trials. Right, mPFC population activity can decode between alone tone presentations and win trials during the competition trials (shuffle performance indicated by gray line; mean AUC vs shuffled AUC Wilcoxon rank sum p=0.0002). j, mPFC population activity is not sufficient to decode early vs late trials within task (alone mean AUC vs shuffle AUC Wilcoxon sum rank p=0.47; comp mean AUC vs shuffle AUC Wilcoxon sum rank p=0.47).
