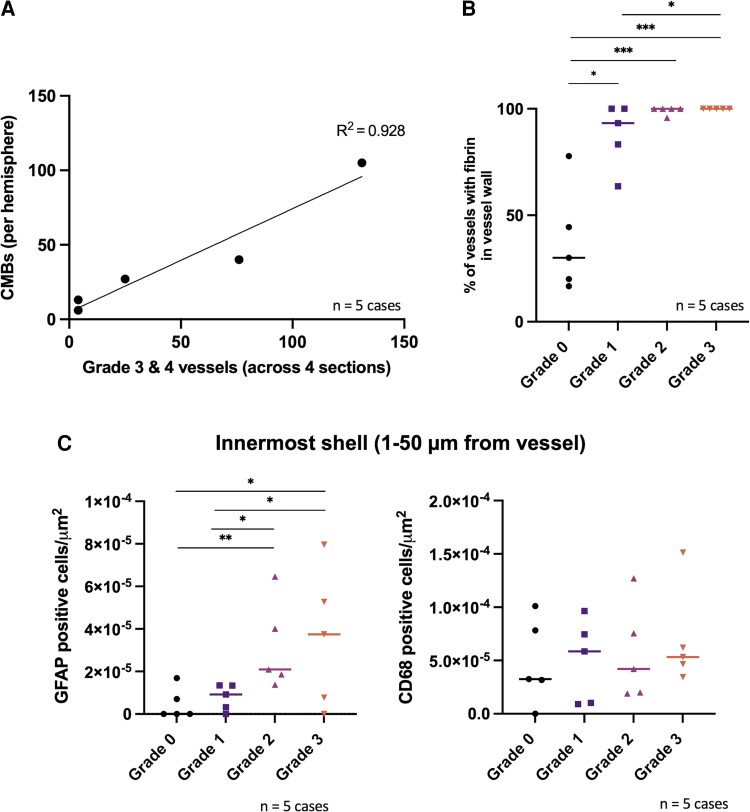
Figure 4.
Advanced grade vessels are associated with higher numbers of microbleeds as well as blood–brain barrier leakage and perivascular inflammation in consecutive CAA cases. (A) Number of CMBs in each hemisphere as compared to the total number of Grades 3 and 4 vessels across four sections taken from standardized regions (frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital) from five consecutive cases with CAA. (B) Per cent of vessels within each vessel grade with evidence of fibrin(ogen) within their vessel wall across five consecutive cases with CAA (median shown) in the occipital cortex. Friedman χ2 (d.f. = 3) = 10.357, P = 0.016 with a large estimated effect size (Kendall’s W = 0.69). Post hoc pairwise comparisons shown using Conover’s test with P-value adjustment (Benjamini–Hochberg). Number of vessels (Cases 3–7): Grade 0 = 5, 10, 6, 9, 9; Grade 1 = 7, 15, 7, 11, 6; Grade 2 = 24, 30, 36, 31, 23; Grade 3 = 22, 4, 3, 1, 7. (C) Density of GFAP-positive cells (left) and CD68-positive cells (right) in the innermost shell surrounding each vessel (1–50 µm from vessel) (median shown). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.005. For GFAP: Friedman χ2 (d.f. = 3) = 9.813, P = 0.020 with a large estimated effect size (Kendall’s W = 0.65). Post hoc pairwise comparisons shown using Conover’s test with P-value adjustment (Benjamini–Hochberg). For CD68: Friedman χ2 (d.f. = 3) = 1.56, P = 0.669) and the estimated effect size was small (Kendall’s W = 0.10). Included in GFAP analysis, number of vessels (Cases 3–7): Grade 0 = 5, 10, 6, 9, 9; Grade 1 = 7, 15, 7, 11, 6; Grade 2 = 24, 29, 35, 30, 22; Grade 3 = 22, 4, 3, 1, 7. Included in CD68 analysis, number of vessels (Cases 3–7): Grade 0 = 5, 9, 5, 6, 7; Grade 1 = 6, 13, 7, 11, 3; Grade 2 = 23, 30, 31, 28, 22; Grade 3 = 22, 4, 3, 1, 7.