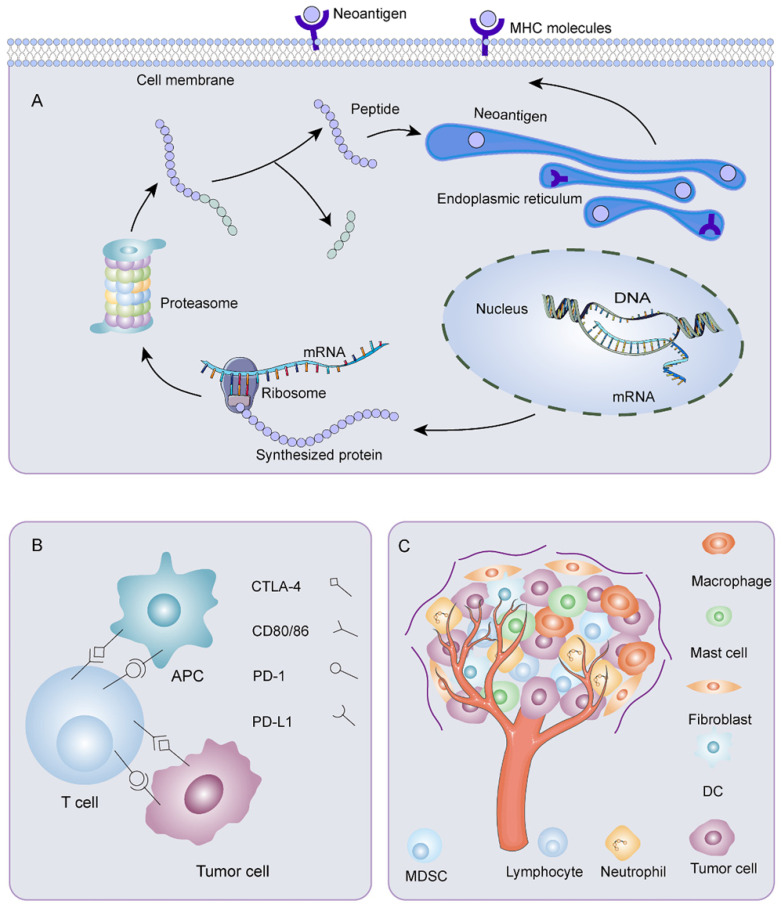
Figure 3.
Mechanisms of immune escape. A) Mutant gene sequences are transcribed and translated into mutated proteins. After processing, the mutant peptides enter the endoplasmic reticulum. They bind MHC I or MHC II to form peptide-MHC molecular complexes, which are transported to the surface of tumor cells. Any abnormality in the process of neoantigen processing and presentation could result in immune escape. B) Overexpression of immune checkpoints restrains anti-tumor immune responses. C) Various components of tumor microenvironment are associated with the occurrence of immune escape.