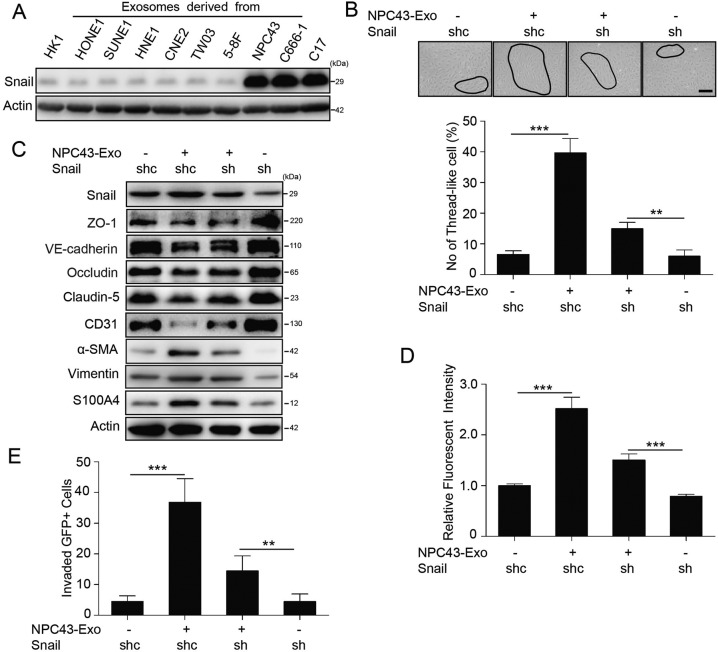
Fig. 4. Exosomal HMGA2 reduces endothelial cell TJ protein expression and promotes EndMT via Snail.
A Top, pathways affected by NPC43 cells derived exosomes in HUVECs compared with HK1 cells derived exosomes and PBS. Bottom, a heatmap of differentially expressed genes involved in selected pathways. B Top, pathways affected by HMGA2 in HUVECs with HMGA2 overexpression compared with the control. Bottom, a heatmap of differentially expressed genes involved in selected pathways. C Western blot analysis of Snail level in HUVECs following treatment with exosomes derived from EBV-negative NPC cells (HK1, HONE1, SUNE1, HNE1, CNE2, TW03 and 5-8F cells) and EBV-positive NPC cells (NPC43, C666-1 and C17 cells). Western blot was conducted three times. D Representative images (high panel) and histogram of the quantification (low panel) of the endothelial cellular morphology alteration after the cells were treated as indicated for 48 h. ***p < 0.001. E HUVECs were infected with shSnail for 48 h and then treated with NPC43-Exo for 48 h. The cell lysate was analyzed by Western blotting for the TJ proteins, CD31, α-SMA, Vimentin and S100A4. Western blotting was conducted three times. F The permeability of HUVEC monolayers treated as indicated was measured by the absorption value of rhodamine-dextran. ***p < 0.001. G HUVEC monolayers grown on 3 μm filters were treated as indicated before GFP-labeled 5-8F cells were seeded in the Transwell inserts. After 10 h, the GFP+ cells on the bottom side of filter were quantified under a fluorescence microscope. ***p < 0.001.