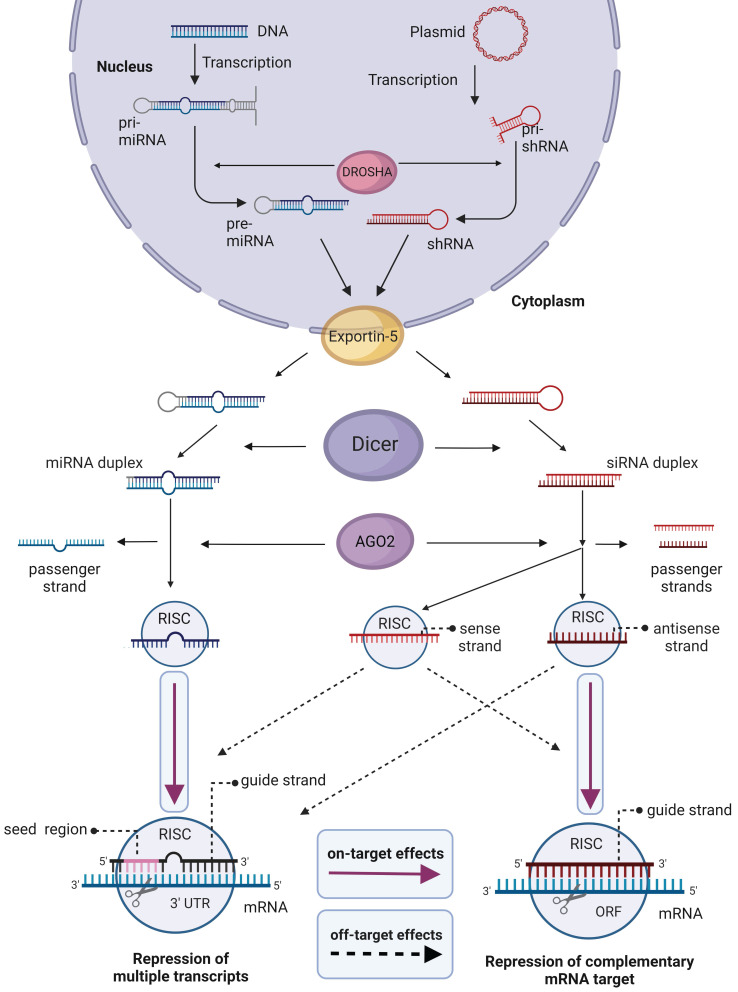
Figure 4.
Biogenesis and effects of siRNA and miRNA in cells. In the nucleus, Drosha endoribonuclease cleaves primary miRNA (pri-miRNA) and the precursor of siRNA (pri-shRNA) to yield 70-100 nt pre-miRNA or shRNA, which are then transported to the cytoplasm by Exportin 5. In the cytoplasm, the RNAs are converted to 18-25 nt bp miRNA or 21-23 bp siRNA by Dicer. For gene silencing and therapy, chemically synthesized mature 19-24 bp siRNA or miRNA can be delivered into cells. Alternatively, cells can be transformed with plasmids coding for pri-shRNA or pri-miRNA that maturate using the same mechanism. RNAi silencing process starts in the cytoplasm by association of siRNA or miRNA with the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). Argonaute 2 (AGO2) component of RISC complex unwinds dsRNA and nicks the passenger sense strand. However, this action is not selective, and the antisense strand of siRNA also may be removed, thus using the sense strand as a guide. The guide strand of siRNA in the active RISC complex binds mRNA target causing its cleavage. RISC/miRNA complex binds 3'-untranslated regions (3' UTR) of mRNA with perfect complementarity in the seed region (2-8 nt site) causing down-regulation of multiple mRNAs. Active RISC/siRNA complex can silence non-targeted mRNA by miRNA-like mechanism. Magenta arrows show specific effects, dashed arrows show HD OTEs.