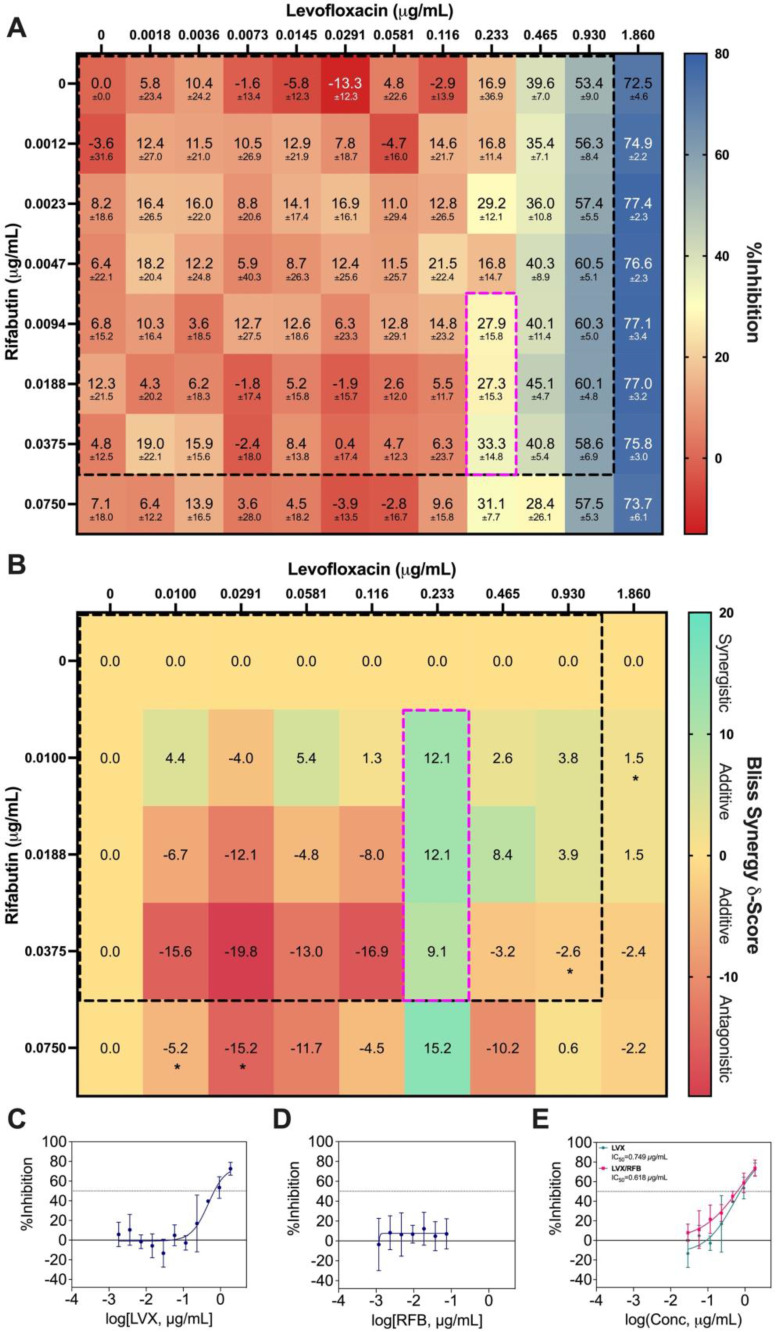
Figure 6.
Bliss independence model analysis of LVX/RFB. (A) Interaction map of LVX/RFB with measured %Inhibitions at each corresponding dose ratio. The %Inhibitions of LVX/RFB combinations and monotherapies were tested from 0% to 20% Cmax, and the clinically actionable interaction space (< 10% Cmax) for LVX/RFB is within dotted black box, which was also the interaction space analyzed by IDentif.AI (N = 3). (B) Synergy map of LVX/RFB with corresponding Bliss Synergy δ-Scores. Scores greater than 10, between -10 and 10, and less than -10 are considered synergistic, additive, and antagonistic, respectively. Bliss independence analysis revealed a mild synergistic dose region (dotted pink box). Clinically actionable interaction space (< 10% Cmax) is within the dotted black box. Statistical significance of the Bliss Synergy δ-Scores was determined by one-sample t-test (*P < 0.05). (C-D) Dose response curves of LVX and RFB in monotherapies. The dotted line represents absolute IC50. Data points are presented as mean ± propagated SD (N = 3). (E) Dose response curve of LVX in monotherapy and in combination with RFB. The IC50 values for LVX and LVX/RFB are summarized in the legend. The dotted line represents absolute IC50. Data points are presented as mean ± propagated SD (N = 3). Experimental data are summarized in Table S7. LVX: levofloxacin and RFB: rifabutin.