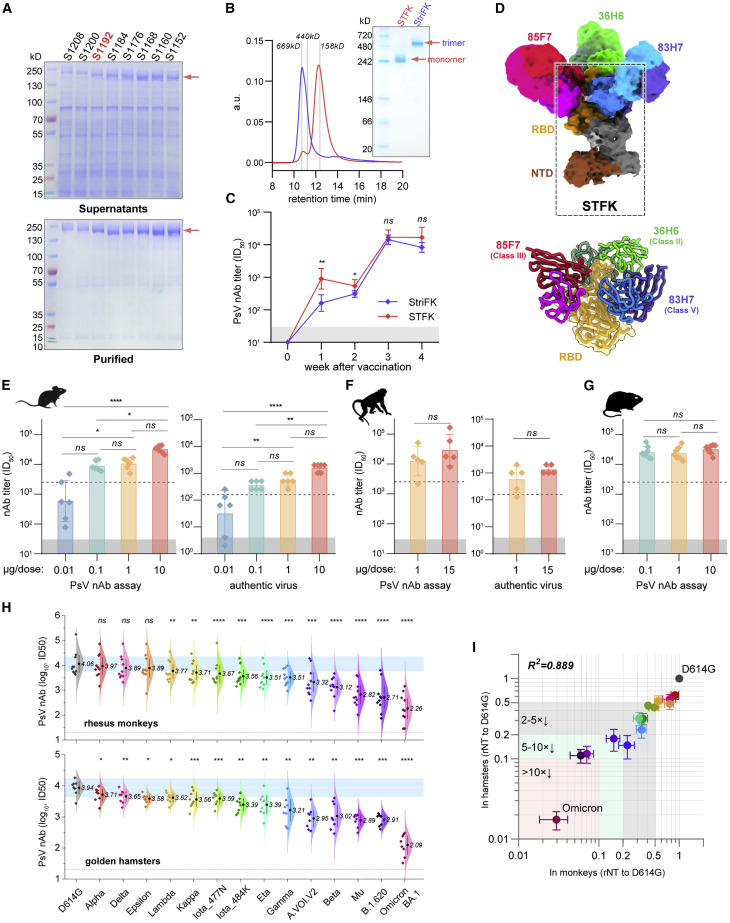
Figure 1.
The monomeric STFK is highly immunogenic in rodents and nonhuman primates
(A) Reduced SDS-PAGE analyses for supernatants (top panel) and purified proteins (bottom panel) produced from constructs encoding progressive truncations from the C terminus of the furin site with mutated spike ectodomain in CHO cells. S1208, aa 1–1,208; S1200, aa 1–1,200; S1192, aa 1–1,192; S1184, aa 1–1,184; S1176, aa 1–1,176; S1168, aa 1–1,168; S1160, aa 1–1,160; S1152, and aa 1–1,152.
(B) Analyses of the monomeric STFK (aa 1–1,192) and trimeric StirFK by SEC-HPLC (left panel) and native-PAGE (right panel).
(C) Comparison of the PsV nAb titers elicited by the STFK and StriFK in mice. BALB/c mice were immunized twice with 1 μg antigen at weeks 0 and 2.
(D) 3.81 Å cryo-EM density map and corresponding atomic model of the STFK in complex of nAbs 36H6, 83H7, and 85F7. The black dotted box highlights the monomeric STFK protein.
(E and F) Serum nAb titers against pseudotyped (left panel) and authentic SARS-CoV-2 viruses (right panel) of (E) BALB/c mice (n = 6) or (F) Rhesus monkeys (n = 5) received 2 shots of STFK vaccinations at different antigen doses.
(G) Serum nAb titers against VSV-based PsV of hamsters vaccinated at 0.1 (n = 8), 1 (n = 7), or 10 μg (n = 8) of STFK per dose. The immunization schedule was week 0/3 for (E) and (G) and week 0/4 for (F). Sera were analyzed at weeks 4 (E), 6 (F), and 5 (G). The dotted lines show the PsV nAb titers of WHO International Standard for anti-SARS-CoV-2 immunoglobulin using the same assays (NIBSC 20/136).
(H) The nAb titers of sera from STFK-vaccinated rhesus monkeys (pooled of 1- and 15-μg groups, top panel) and hamsters (10-μg group, bottom panel) against lentiviral-pseudotyped SARS-CoV-2 spike variants compared with that against the ancestral D614G strain. The numbers showed the nAb GMT (log10) values.
(I) Comparison of the cross-neutralizing activities of vaccinated hamsters (x axis) and rhesus monkeys (y axis) against various lentiviral-pseudotyped SARS-CoV-2 variants. The relative nAb titer (rNT) was calculated as its ID50 ratio against a variant to the D614G control for each sample. Data in (D)–(H) were plotted as the geometric mean with SD. Dark shadows in (D)–(G) indicate the limit of detection (LOD). The dotted line in (H) indicates the LOD. Blue shadows in (H) represent the range of 50%–200% (within 2-fold changes) of the nAb GMT against D614G (as white line indicated). Uncorrected Kruskal-Wallis test (D, E, and G), Mann-Whitney U test (F), or Dunnett's multiple comparison test (H) were used for intergroup statistical comparisons. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗p < 0.05; ns, not significant). Silhouettes indicating the species in (E)–(G) were from PhyloPic.org and available under the Public Domain Dedication 1.0 license.
See also Figure S1.