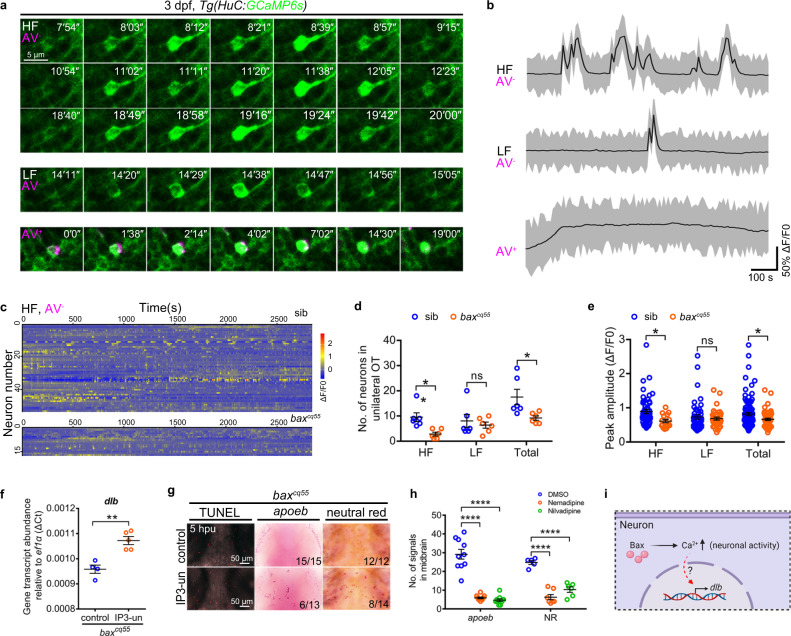
Fig. 5. Bax drives dlb expression via a special type of neuronal activities.
a Confocal time-lapse imaging of GCaMP6s+ signals (green) in HF (top), LF (middle) and AV+ apoptotic neurons (bottom, magenta) in the midbrains. The number in the up-right corner indicated the time pointes. b Representative patterns of Ca2+ events in the HF, LF, and AV+ neurons during 1000 seconds of imaging. c GCaMP6s+ traces of HF neurons in the unilateral midbrains of 3 dpf siblings and baxcq55 mutants (n = 6 per group). d The number of HF, LF, and total active neurons in the unilateral midbrains of 3 dpf siblings and baxcq55 mutants. Each dot denotes one fish (n = 6 per group). e Quantification of the peak amplitude of calcium events (ΔF/F0) of HF, LF, and total calcium events in the unilateral midbrains of 3 dpf siblings and baxcq55 mutants (n = 6 fish in each group). Each dot denotes one calcium event. f qPCR result of the dlb transcriptional level at 5 hpu. The data are from three independent experiments. Each dot represents an independent experiment. g Representative images of apoeb WISH, NR and TUNEL staining in the midbrains of baxcq55 mutant at 5 hpu. h Quantification of apoeb+ and NR+ signals after application of nemadipine and nivadipine. Each dot denotes one fish (apoeb: n = 10 per group; NR: DMSO: n = 5, nemadipine: n = 7, nilvadipine: n = 6). i Schematic presentation of Bax regulating dlb via neuronal activity, created with BioRender.com. HF high frequency, LF low frequency, AV Annexin V, IP3-un IP3 uncaging, hpu hours post-uncaging. Numbers in the right corners in (g) indicate the counts of embryos with a typical appearance (first number) in the total examined fishes (last number). Error bars, mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001; ns no significant, Unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.