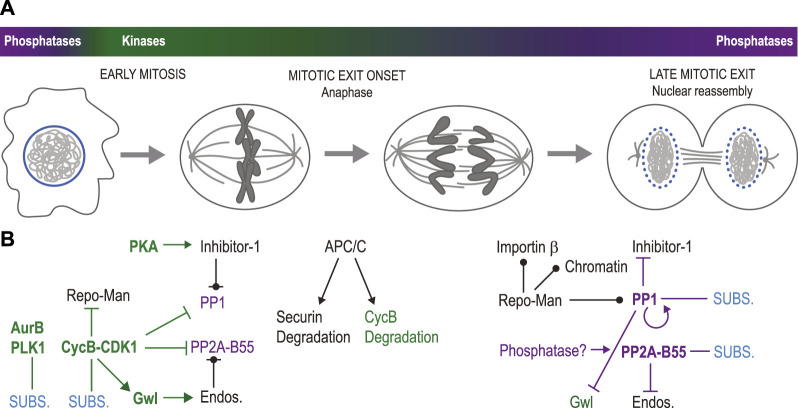
FIGURE 2.
Elements of temporal regulation in nuclear reassembly. (A). During mitotic entry, mitotic kinases become more active while some mitotic phosphatases become less active, causing NEBD, chromosome condensation and spindle assembly. Mitotic exit begins with anaphase onset, followed by nuclear reassembly. During mitotic exit, mitotic kinases become generally less active while phosphatases regain their full activity. (B). Molecular networks at play in the transitions displayed in panel (A). At the beginning of mitosis (left), Cyclin B-CDK1, Aurora B, PLK1 and other mitotic kinases phosphorylate multiple substrates (SUBS.) leading to the disassembly of the interphase nucleus. Concomitantly, PP1 and PP2A-B55 are inhibited. PP1 phosphorylation by Cyclin B-CDK1 inhibits its activity. PP1 is also inhibited by Inhibitor-1 phosphorylated by PKA. Repo-Man, the PP1 regulatory subunit, is phosphorylated at multiple CDK sites that inhibit its interactions with PP1, its targeting to chromatin and its interaction with Importin β. CDK1-activated Gwl kinase phosphorylates Endosulfine proteins (Endos.) which then inhibit PP2A-B55. CDK1 also inhibits PP2A-B55 complex formation by phosphorylating PP2A-C. At the onset of mitotic exit (center), anaphase is triggered by the activation of the APC/C, which promotes the degradation of Securin, allowing sister chromatid separation. Cyclin B is also largely degraded at this time in an APC/C-dependent manner. At later stages of mitotic exit (right), PP1 dephosphorylates itself, thereby becoming active. It also dephosphorylates Inhibitor-1 (relieving inhibition), Repo-Man (allowing it to interact with PP1, chromatin and Importin β) and Gwl (inactivating it). Endosulfines dephosphorylation by PP2A-B55 may then be completed, relieving PP2A-B55 inhibition. At that stage, PP1 and PP2A-B55 can dephosphorylate several proteins to promote nuclear reassembly. The phosphatase responsible for PP2A-C dephosphorylation is unknown. Green names: kinases; purple names: phosphatases; bold names: active enzymes; pointed arrows: activation; blunt-ended arrows: inhibition: circle-ended arrows: interaction; green connections: phosphorylation; purple connections: dephosphorylation.