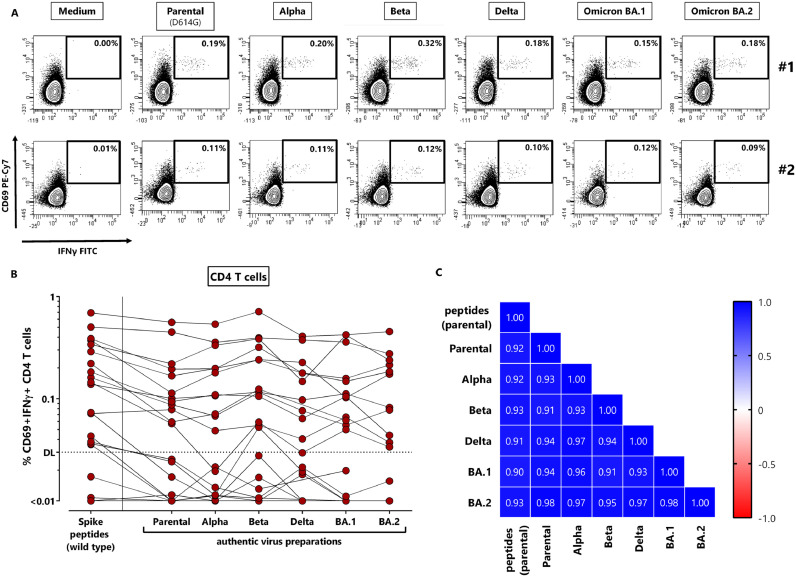
Fig. 4.
NVX-CoV2373-induced T-cells equally recognize parental SARS-CoV-2 and variants of concern. Whole blood samples of 22 NVX-CoV2373-vaccinated individuals 13–18 days after the second vaccination were stimulated with overlapping peptides of parental SARS-CoV-2 spike or UV-inactivated parental SARS-CoV-2 or variants of concern. (A) Dotplots of two individuals with detectable spike-specific CD4 T-cells are shown (#1: 56 year old female, #2: 32 year old male). Percentages of activated (CD69+) cells producing IFNγ among CD4 T-cells are shown after stimulation with medium (negative control), parental SARS-CoV-2 or variants Alpha, Beta, Delta, Omicron BA.1 and BA.2. (B) Specific CD4 T-cells were quantified for all individuals based on co-expression of CD69 and IFNγ with respective reactivity after control stimulation subtracted. Indeterminate results of one person had to be excluded due to excessive background reactivity in the medium control; Delta and BA.2 stimulations were available from 19 individuals only. (C) Correlation matrix of specific T-cell levels determined after stimulation with spike-peptides and the different UV-inactivated virus preparations. Correlation coefficients were calculated according to two-tailed Spearman and displayed using a color code. IFN, Interferon.