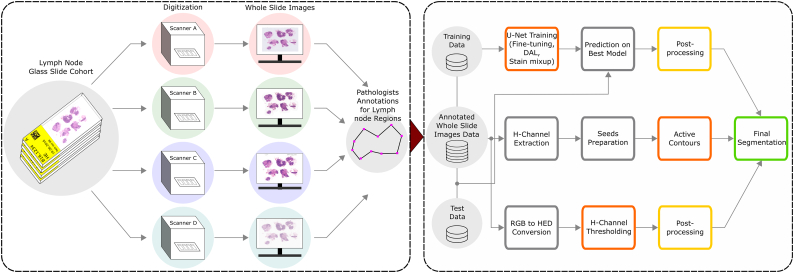
Fig. 1.
The workflow to assess the impact of scanner variability on lymph node segmentation. Same lymph node glass slide cohort is digitized using 4 different scanners and given to expert pathologists for lymph node annotations. The annotated WSI are then distributed into test and train sets to evaluate the scanner variability with the help of 3 different segmentation methods (i.e. core method in orange color): Hematoxylin-channel-based thresholding (HCT), Hematoxylin-based active contours (HAC), and a convolution network (U-Net). In order to minimize scanner variability, the segmentation methods are evaluated with normalization, fine-tuning, domain adversarial learning, and stain mix-up experiments. Upon application of segmentation methods, the post-processing (i.e in yellow color) is used for HCT and U-Net to achieve final segmented nodes (i.e in green color) by eliminating the undesired pixels around the region of interests. The HAC method uses an iterative smoothing operator and does not require final post-processing step.