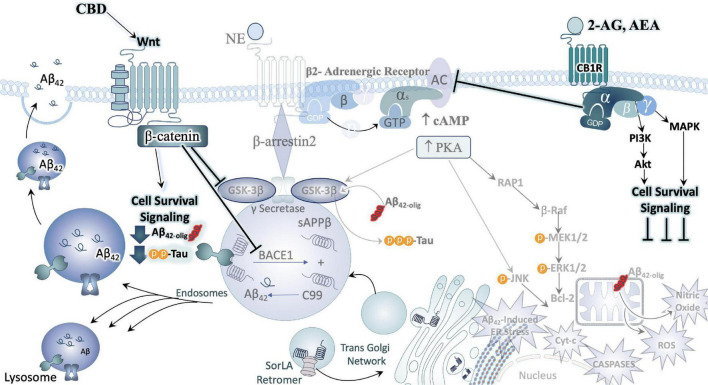
FIGURE 6.
Cannabinoids counteract AD neuropathology exacerbated by stress. In direct opposition to (chronic) stress-responsive intracellular signaling cascades such as those downstream of the adrenergic receptors (ARs) or CRFR1, Cannabinoids inhibit cell signaling cascades that promote neuronal cell death. A major effector engaged by cannabidiol (CBD) exposure is the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. By binding its cognate receptor and co-receptor, Wnt increases the level of stable intracellular β-catenin proteins. β-catenin then goes on to inhibit GSK3β, the enzyme responsible for the upregulation of tau-phosphorylation, inhibit the beta-secretase (BACE-1), and promote the neuroprotective alpha-secretase cleavage of APP (not depicted here). Moreover, activation of CB1 receptors (CB1R) can counteract excessive stimulatory G-alpha subunit signaling by inhibiting adenylyl cyclase (AC) activity. By engaging the mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) and Akt pathways, CB1R signaling instead promotes the production and release of protective, cell survival factors.