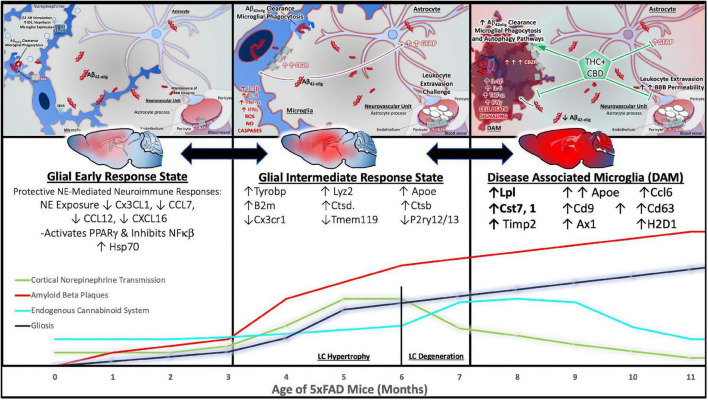
FIGURE 7.
Inflammatory progression in 5xFAD AD mouse model and beneficial effects of cannabinoids. The time course of neuropathology and inflammation in the 5xFAD model of AD LC-NE modulation of inflammation, LC degeneration, and the development of degeneration-associated microglial (DAM) phenotypes that have been defined by single-cell RNA polymerase experiments. 5xFAD mice develop cerebral amyloid plaques and gliosis by 2 months, exhibit reduced synaptic markers, neuronal loss and memory impairment by 4 months, and continue to accumulate extra- and intraneuronal Aβ42 between 12 and 16 months of age. While intact, the LC-NE system is neuroprotective. NE mediates an increase in protein expression of the 70 kilodalton heat shock protein 70 (hsp70), and a reduction of nitric oxide synthase (NOS). By 3 months, 5xFAD mice show a significant increase in CB2r (Panel 1, left). By 5 months there is significant evidence of LC damage and inflammation. At 6 months, studies have demonstrated a shift in microglia phenotype from a homeostatic or early response state to an intermediate response state, and this transition is defined by the upregulation of AD-associated genes (B2m,Ctsd,Ctsb, Fth1, Tyrobp and apoe) and concurrent downregulation of the homeostatic CxCL1, P2ry12/P2ry13, and Tmem119 genes (Panel 2, center). 5xFAD mice show intrinsically decreased CB1r, decreased MAGL, increased DAGL and increased CB2r expression at 11 months. Studies evaluating microglial phenotypes in 5xFAD mice at 8 months show a distinct, TREM-2 dependent transition to the late response state known as DAM. The DAM phenotype is characterized by an increase in AD associated genes such as Lpl, apoe, and the TREM2-Tyrobp signaling complex. Importantly, a recent study demonstrates that in the 5xFAD model, CBD could improve the behavioral and cognitive function of AD mice by modulating the expression of IL-5 (Khodadadi et al., 2021). Other mechanisms of CBD + THC mediated protection include the reduction of inflammatory cytokines, promoting autophagy and microglial phagocytosis of amyloid plaques and maintaining blood brain barrier integrity by preventing leukocyte extravasion (Panel 3, right).