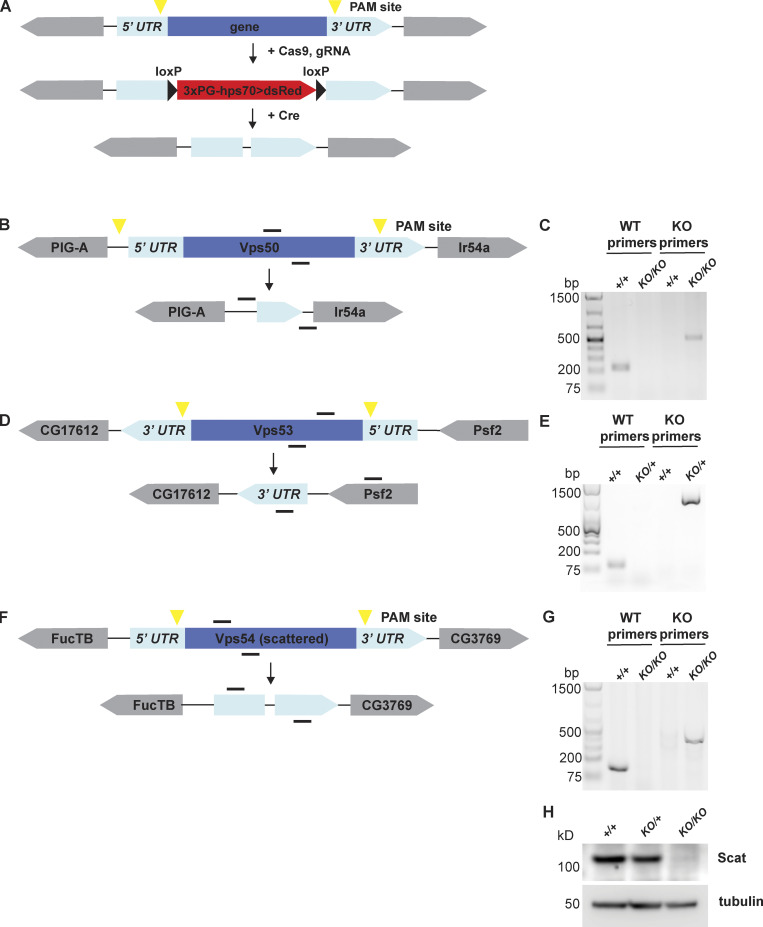
Figure S1.
Generation of GARP and EARP knockout flies. (A) General schematic of CRISPR knockout strategy. Guide RNAs recognize sequences around PAM sites (yellow triangles). DsRed cassette flanked by loxP sites was knocked-in in place of the gene of interest to generate DsRed+ knockout (KO) lines. DsRed cassette was removed by crossing to a Cre recombinase line to generate the final knockouts. (B, D, and F) Schematic of Vps50, Vps53, and scattered (Vps54) wild-type genes and knockouts, respectively. Genes are shown in their relative orientation in the genome. Black lines above indicate hybridization sites for genotyping primers. (C, E, and G) Agarose gel of genotyping PCR for Vps50, Vps53, and Vps54 knockout lines, respectively. +/+ = w1118. For Vps50 and Vps54, DNA was isolated from adult males. Because Vps53KO is lethal in the pupal stage, DNA was isolated from wandering third instar larvae. Bp = base pairs. (H) Western blot of head lysates from control, Vps54KO/+ and Vps54KO/KO larvae probed with antibodies raised against Vps54/scattered and tubulin (loading control). See Table S1 for cloning and genotyping primer sequences. Source data are available for this figure: SourceData FS1.