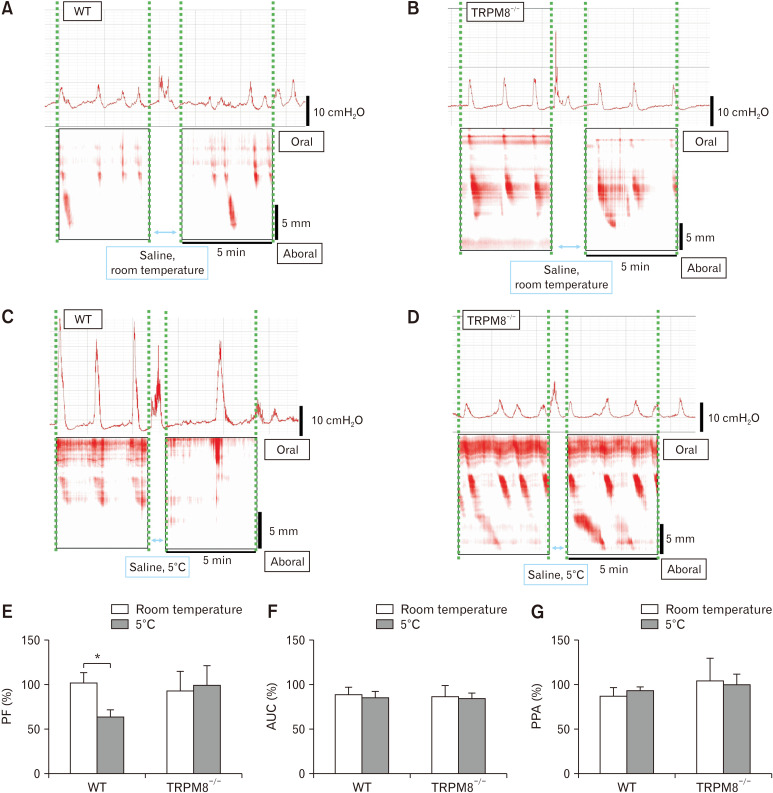
Figure 5.
Colonic motility in wild type (WT) mice and transient receptor potential melastatin 8 (TRPM8)-deficient (TRPM8–/–) mice. The intraluminal high-amplitude pressure and colonic motor activity before and after administration of 5°C saline in wild type (WT) mice. A typical pattern of reduction of colonic motor activity and intraluminal high-amplitude pressure induced by 5°C saline. (D) The colonic motility and intraluminal high-amplitude pressure before and after administration of 5°C saline in transient receptor potential melastatin 8-deficient (TRPM8)–/– mice. (E) Decreased ratio of peak frequency (PF) in high-amplitude pressure following administration of 5°C saline in WT mice. To quantify the decrease in high-amplitude pressure induced by 5°C saline, the ratio of contraction frequency before and after administration with a length of more than 8 mm was calculated as the %PF. *P < 0.05 vs room temperature (25°C) of wild type mice. (F) The area under the curve (AUC) at high-amplitude pressure with 5°C saline. The AUC was calculated before and after saline administration using the lowest intraluminal pressure value as the baseline. There were no significant differences between the 2 groups. (G) The results of the peak pressure amplitude (PPA) at high-amplitude pressure with 5°C saline. The difference between PPA and the lowest intraluminal pressure was defined as PPA, and the ratio of PPA before and after medication was calculated as %PPA. There were no significant differences between the 2 groups (n = 6).