FIGURE 2.
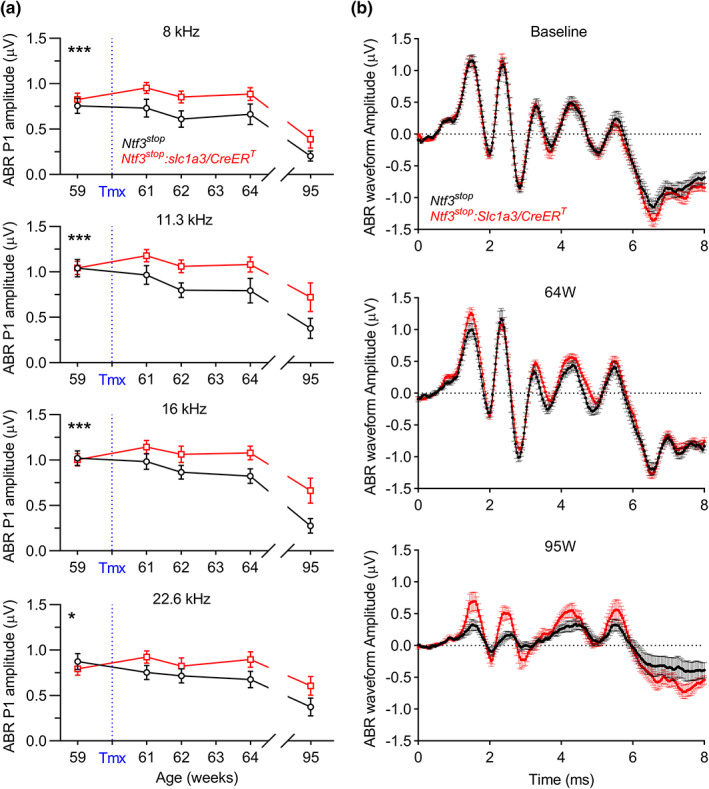
Sound‐evoked activity along the cochlear axis, and in higher auditory centers in the aging brain, is higher in aging Ntf3 overexpressing mice than in age‐matched controls. (a) After tamoxifen treatment at 60 weeks of age, ABR peak 1 amplitudes along the cochlear axis are larger in Ntf3 stop :Slc1a3/CreER T mice than in Ntf3 stop age‐matched controls. 2‐way ANOVA followed by Sidak's multiple comparisons test was used to evaluate ABR peak 1 amplitudes between groups over time at each individual cochlear region (frequency, kHz). (b) Mean ABR waveforms recorded at 59 (baseline), 64 and 95 weeks of age show that mice with Ntf3 overexpression have larger sound‐induced ABR peaks along the ascending auditory pathway as they age. At baseline, before tamoxifen treatment, no intergroup differences were seen in ABR waveforms (also see Figure S2). At 64 weeks, peak 1 amplitudes were increased in Ntf3 overexpressing mice. At 95 weeks, Ntf3 overexpressors exhibited smaller decreases in ABR peaks 1, 2, and 4 than Ntf3 stop controls (also see Figure S2). ABRs shown here are group means in response to 16 kHz tone pips at 80 dB SPL. Ntf3 stop n = 7–13 mice; Ntf3 stop :Slc1a3/CreER T n = 7–17 mice. * p < 0.05; *** p < 0.001. Error bars represent SEM
