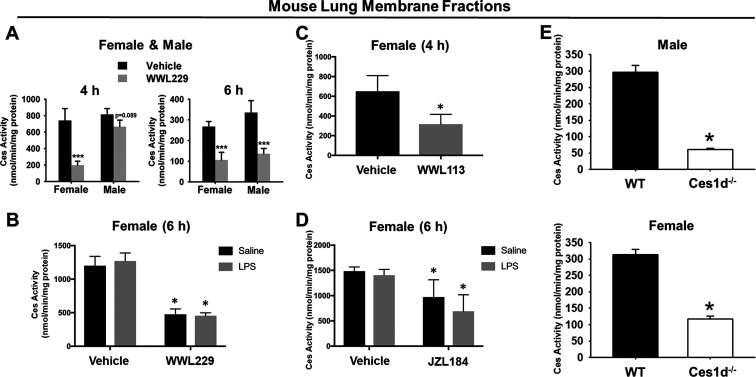
Figure 4.
Ces activity in lung membranes from vehicle- and inhibitor-treated WT mice and Ces1d−/− mice. (A) Lung Ces activity was reduced in WT mice by WWL229 in a sex-dependent and -independent manner at 4 h and 6 h, respectively. (B) Intraperitoneal LPS challenge had no effect on lung Ces activity in female mice, and it did not alter WWL229-mediated Ces inhibition. Lung Ces activity was inhibited in female mice by WWL113 (C) and JZL184 (D). Lung Ces activity in Ces1d−/− mice were markedly lower than those in WT mice (E). Data are expressed as the mean ± SD [n = 5 mice, n = 3 male mice at 4 h, (A); n = 3 mice, (B,C); n = 5 mice, (D,E)]. One-way ANOVA (C,E) or two-way ANOVA (A,B,D) assessed significant differences between groups. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 for treatments vs vehicle or Ces1d−/− vs WT.