Figure 1.
Specificity of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies induced after SARS-CoV-2 infection versus vaccination
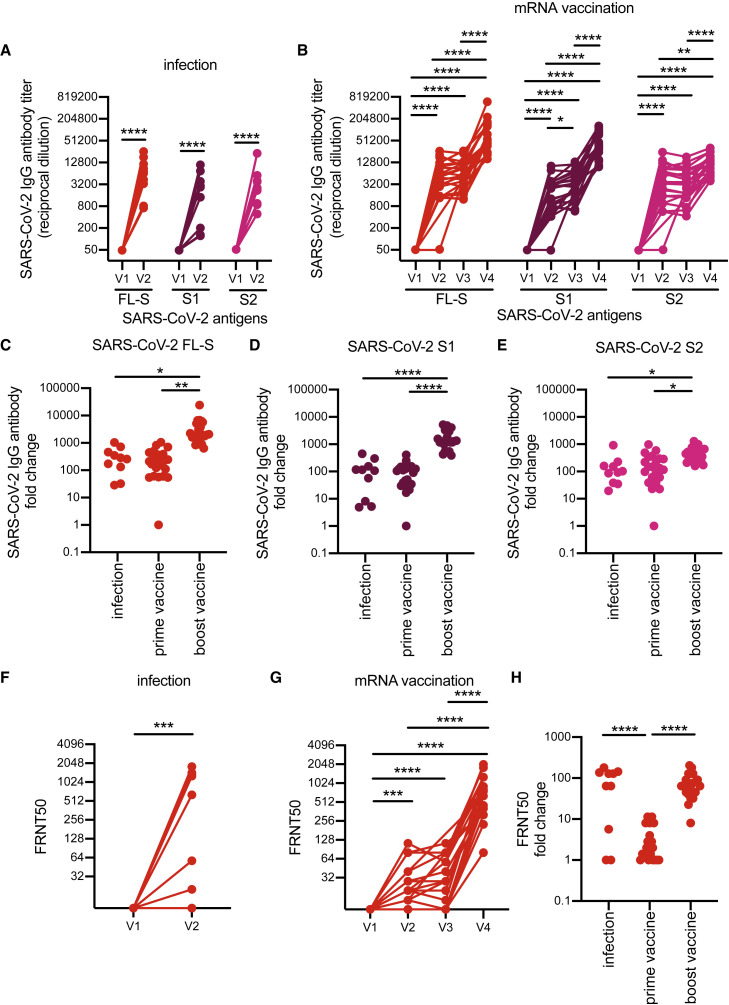
(A and B) ELISAs were completed to quantify levels of serum antibodies binding to the SARS-CoV-2 full-length spike (FL-S) protein, the S1 domain (S1) of S, and the S2 domain (S2) of S after SARS-CoV-2 infection (A) and mRNA vaccination (B).
(C–E) We calculated fold change in antibody titers before and after seroconversion and pre-/post-prime and boost doses of a SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine.
(F and G) SARS-CoV-2 pseudotype neutralization assays were completed with sera samples from SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals (F) and SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-vaccinated participants (G).
(H) Fold change in neutralization titers was calculated before and after seroconversion and pre-/post-prime and boost doses of a SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine.
For (A), (B), (F), and (G), we completed paired t tests or one-way ANOVA of log2-transformed titers; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗p < 0.05. For (C)–(E) and (H), we completed one-way ANOVA of titer fold changes; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, ∗∗p < 0.01 ∗p < 0.05. Data are representative of two independent experiments. Neutralizing antibody titers of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccinated participants have been previously reported in Goel et al. (2021a).