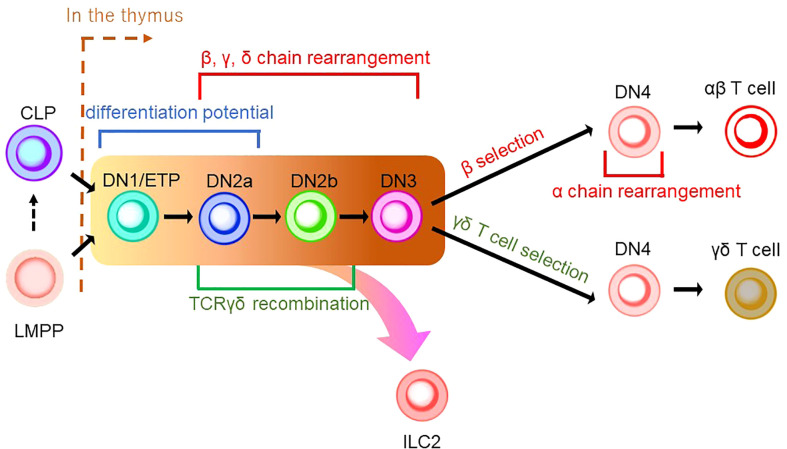
Figure 2.
A schematic model of thymic development of T-cell lineages. CLP or LMPP is seeded into the thymus to become a thymocyte (the right side of a brown dashed line indicates thymic development). Thymocyte develops from a series of double-negative (DN) cells. αβ T cells and γδ T cells share the same developmental pathway from DN1/ETP to DN3 (indicated by the background in yellow to brown). DN1/ETP and DN2a harbor the differentiation potential as EILP in mice and EToP1/2 in humans (see Figure 1 ). T-cell receptor (TCR) recombination occurs during DN cell phases. Specifically, DN2a/b and DN3 undergo recombination of β, γ, and δ chains, while DN4 cells in the β-selection pathway do that of the α chain. TCRγδ recombination is known to occur in the phase between DN2a/b. In DN4 stage, γδ T-cell selection induces γδ T-cell development, while β-selection leads to αβ T-cell differentiation. ILC2 may be derived from the transition between the DN1/early thymic progenitor (ETP) and DN3 in the γδ T-cell development pathway.