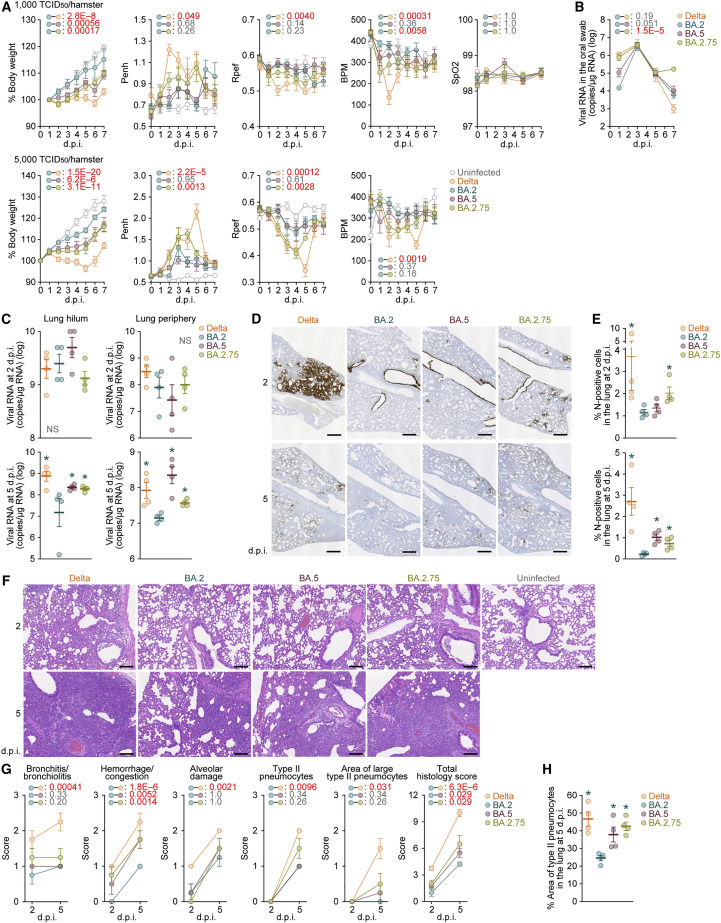
Figure 5.
Virological characteristics of BA.2.75 in vivo
Syrian hamsters were intranasally inoculated with Delta, BA.2, BA.5, and BA.2.75. Two different doses of inoculum (1,000 TCID50/hamster [A, top and B–G] or 5,000 TCID50/hamster [A, bottom]) were used. Six hamsters per infection group were used to routinely measure the respective parameters (A and B). Four hamsters per infection group at a lower inoculum (1,000 TCID50/hamster) were euthanized at 2 and 5 d.p.i. and used for virological and pathological analysis (C–G).
(A) Body weight, Penh, Rpef, BPM, and SpO2 values of infected hamsters (n = 6 each). The results at a low inoculum (1,000 TCID50/hamster) and a high inoculum (5,000 TCID50/hamster) are shown in the top and bottom panels, respectively.
(B) Viral RNA loads in the oral swab (n = 6 each).
(C) Viral RNA loads in the lung hilum (left) and lung periphery (right) of infected hamsters (n = 4 each) at 2 d.p.i. (top) and 5 d.p.i. (bottom).
(D and E) IHC of the viral N protein in the lungs at 2 d.p.i. (top) and 5 d.p.i. (bottom) of all infected hamsters. (D) Representative figures. N-positive cells are shown in brown. (E) Percentage of N-positive cells in whole lung lobes (n = 4 each). The raw data are shown in Figures S5B and S5C.
(F and G) (F) H&E staining of the lungs of infected hamsters. Representative figures are shown. Uninfected lung alveolar space and bronchioles are also shown. (G) Histopathological scoring of lung lesions (n = 4 each). Representative pathological features are reported in our previous studies (Kimura et al., 2022c; Yamasoba et al., 2022a; Suzuki et al., 2022; Saito et al., 2022).
(H) Type II pneumocytes in the lungs of infected hamsters. The percentage of the area of type II pneumocytes in the lung at 5 d.p.i. is summarized. The raw data are shown in Figure S5D.
In (A)–(C), (E), (G), and (H), data are presented as the average ± SEM. In (C), (E), and (H), each dot indicates the result of an individual hamster.
In (A), (B), and (G), statistically significant differences between BA.2 and other variants across time points were determined by multiple regression. In (A), the 0 d.p.i. data were excluded from the analyses. FWERs calculated using the Holm method are indicated in the figures.
In (C), (E), and (G), the statistically significant differences between BA.2 and other variants were determined by a two-sided Mann-Whitney U test.
In (D) and (F), each panel shows a representative result from an individual infected hamster. Scale bars: 500 μm in (D) and 200 μm in (F).
See also Figure S5.