FIGURE 3–3.
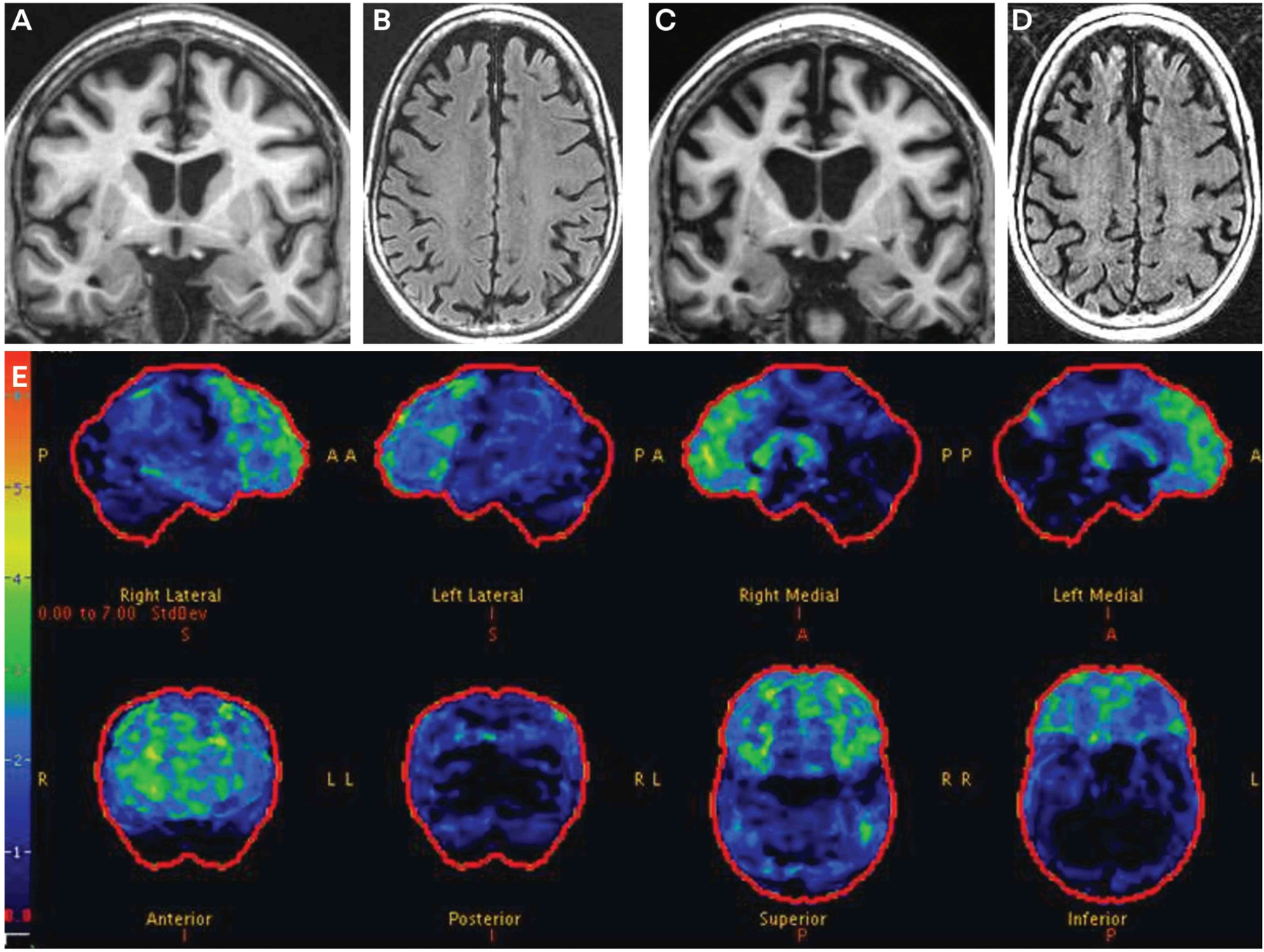
Imaging of the patient in CASE 3-3. Coronal T1-weighted (A) and axial fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) MRI (B) at age 61 show obvious frontal atrophy and more subtle amygdala atrophy. Coronal T1-weighted (C) and axial FLAIR MRI (D) at age 63 show progression of the frontal atrophy, with more obvious temporal atrophy. The lateral ventricles have also increased in size. Fludeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) (E) at age 61 shows mild to moderate hypometabolism in the frontal regions. The color bar and z score reference on the far left of the FDG-PET image reflects the degree of FDG hypometabolism, with blue reflecting z scores in the −1 to −2 range and red reflecting a z score of −6. Therefore, the regions with gray or black color reflect normal metabolism, blue color reflects slight to mild hypometabolism, and green to yellow to red color reflects moderate to very severe hypometabolism.
