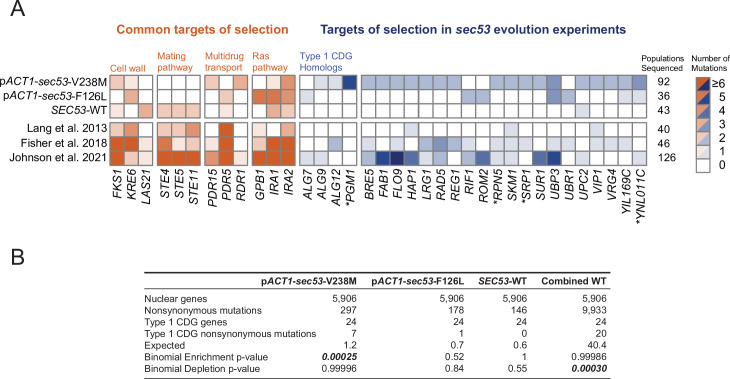
Figure 2. Mutations in Type 1 congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG) homologs are enriched in sec53-V238M populations.
(A) Heatmap showing the number of nonsynonymous mutations per gene that arose in the evolution experiment. Genes with two or more unique nonsynonymous mutations (and each Type 1 CDG homolog with at least one mutation) are shown. pSEC53-SEC53-WT and pACT1-SEC53-WT are grouped as ‘SEC53-WT’. For comparison, we show data from previously reported evolution experiments where the experimental conditions were identical to the conditions used here, aside from strain background and experiment duration (bottom three rows). Commonly mutated pathways are grouped for clarity. Asterisks (*) indicate previously known SEC53 genetic interactors (Costanzo et al., 2016; Kuzmin et al., 2018). (B) Binomial test for enrichment or depletion of mutations in Type 1 CDG homologs based on the number of nonsynonymous mutations observed in each experiment, the total number of yeast genes (5906), and the number of genes that are Type 1 CDG homologs (24). ‘Combined WT’ includes the SEC53-WT populations as well as three additional datasets: Lang et al., 2013, Fisher et al., 2018, and Johnson et al., 2021.
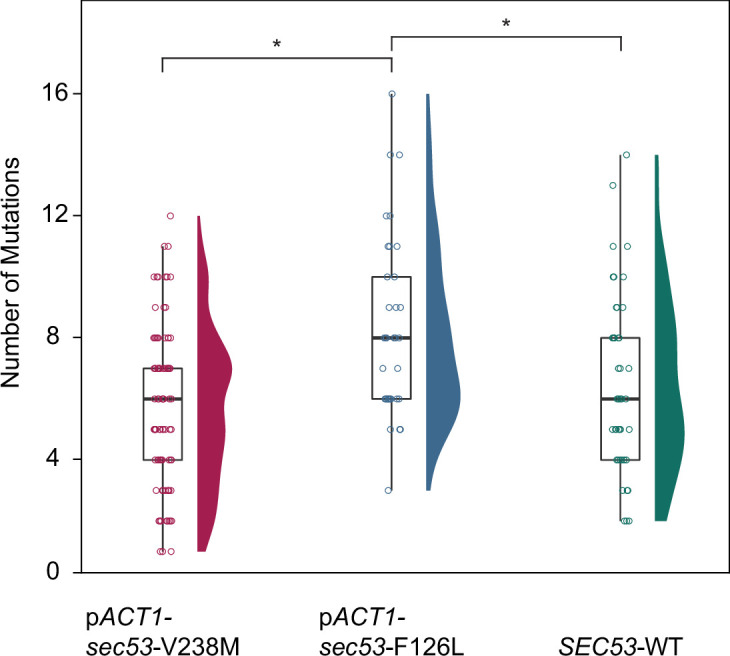
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. The number of de novo mutations per SEC53 genotype.