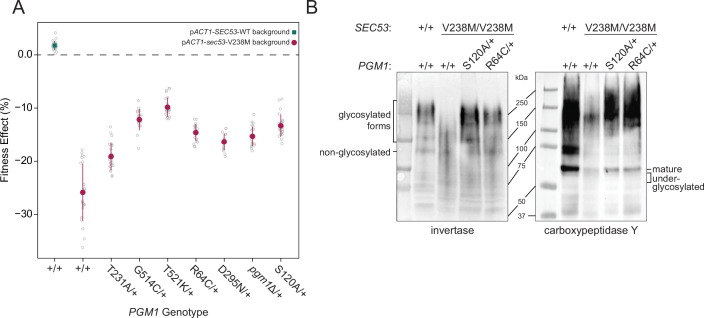
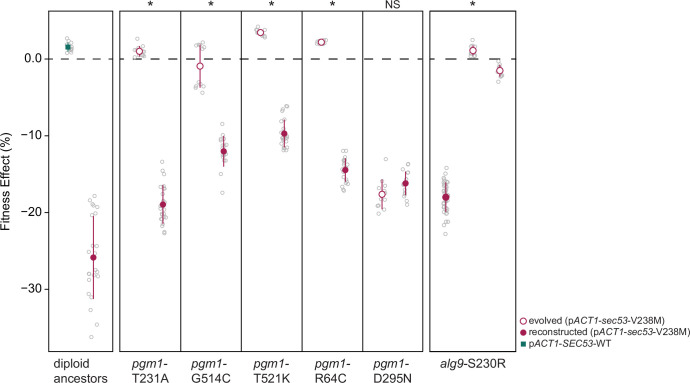
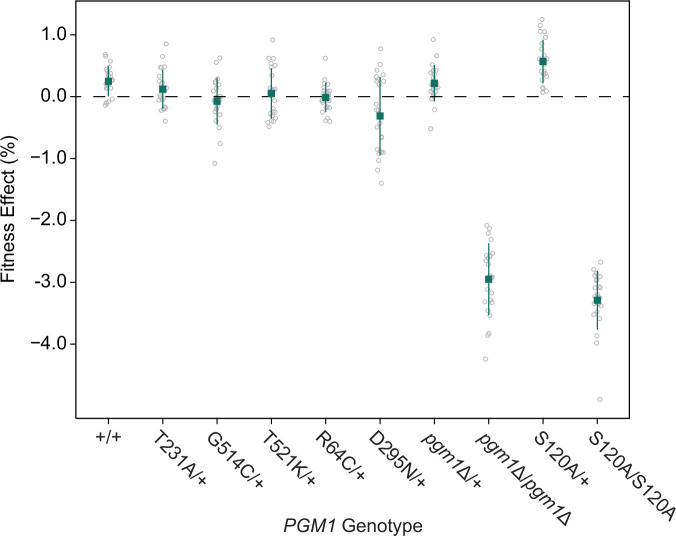
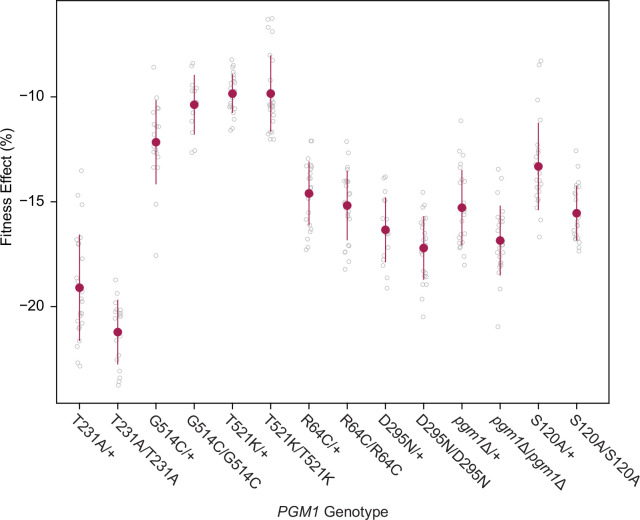
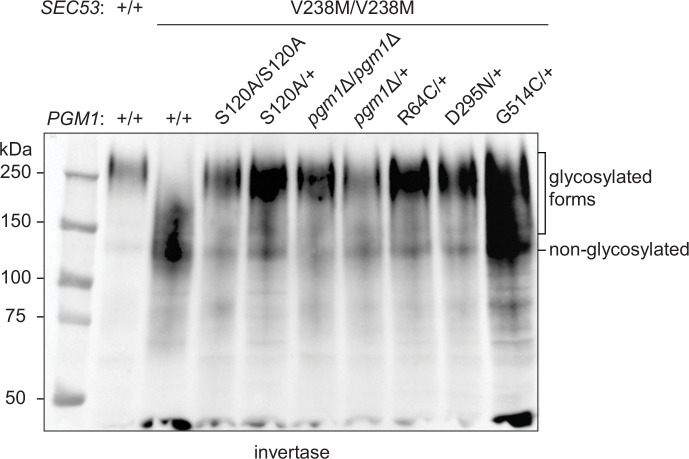
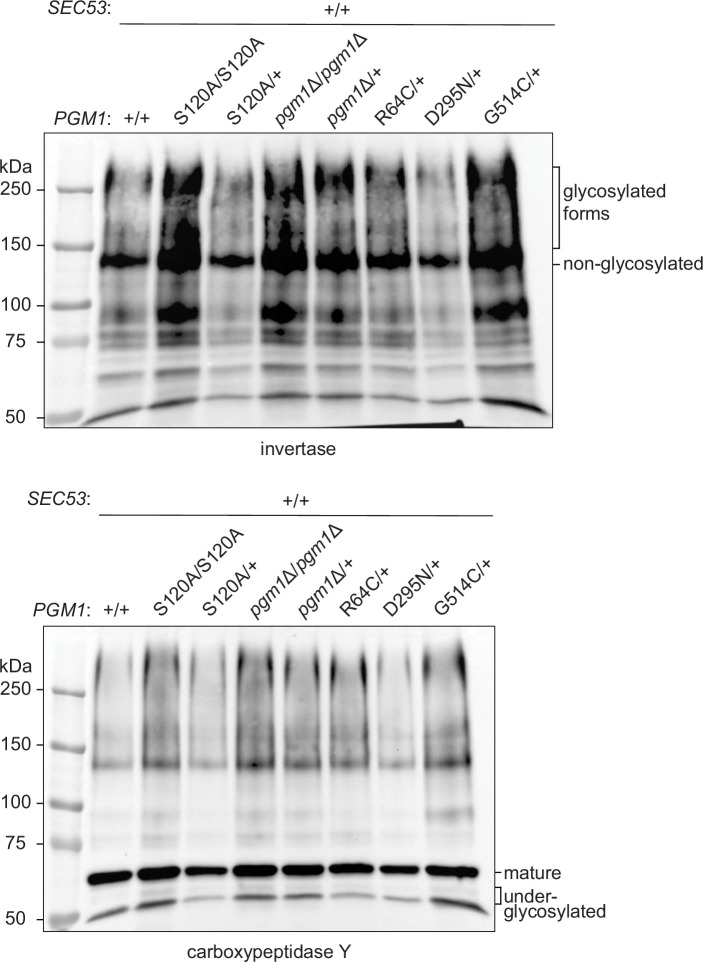
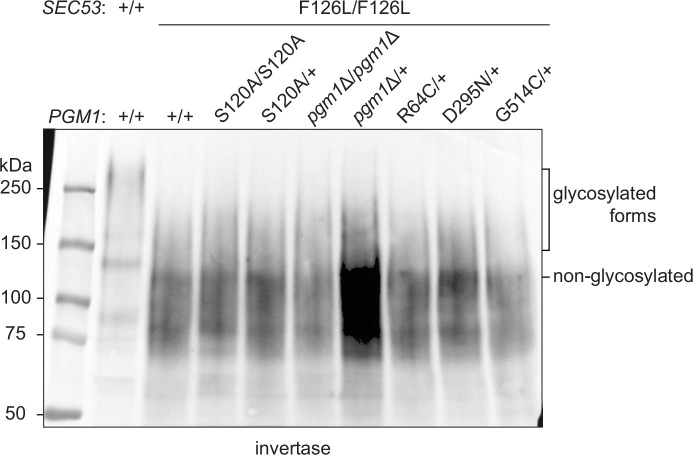
Figure 3. Evolved mutations rescue fitness and protein glycosylation defects of pACT1-sec53-V238M.
(A) Average fitness effects and standard deviations of reconstructed heterozygous pgm1 mutations. Fitness effects were determined by competitive fitness assays against a fluorescently labeled version of the diploid pACT1-SEC53-WT ancestor. Replicate measurements are plotted as gray circles. Pairs of pgm1 fitness effects with non-statistically significant differences: R64C-D295N, R64C-pgm1Δ, R64C-S120A, D295N-pgm1Δ, G514C-T521K, G514C-S120A, and pgm1Δ-S120A (df = 194, F = 208.1, each p > 0.05, one-way analysis of variance [ANOVA] with Tukey post hoc test). (B) Western blots of invertase (left) and carboxypeptidase Y (right) from ancestral and reconstructed strains. In panels A and B, plus signs (+) indicate wild-type alleles. Genotypes are either homozygous wild-type (+/+), homozygous mutant (mutation/mutation), or heterozygous (mutation/+).