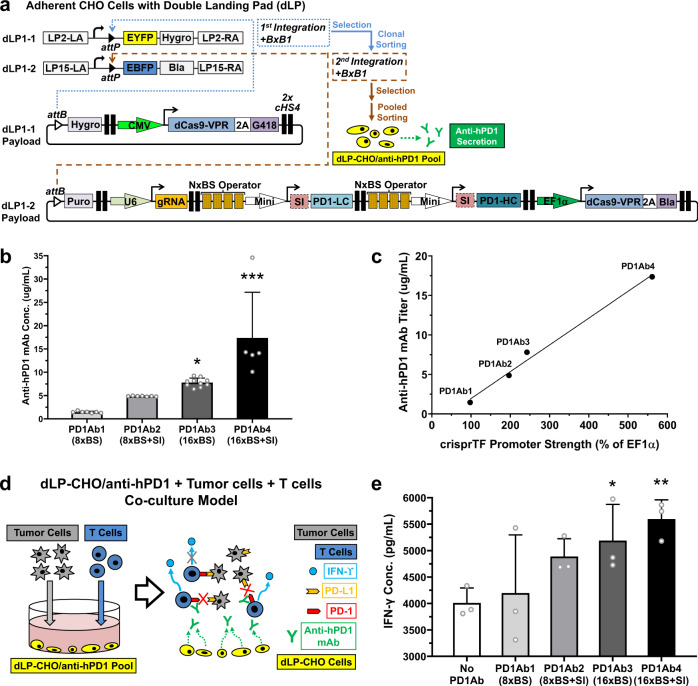
Fig. 6. Programmable control of anti-hPD1 secretion and the human T-cell anti-tumor response.
a Schematic illustration of engineering the anti-hPD1-secreting dLP-CHO cells with sequential and site-specific integration of two payload gene circuits with BxB1 integrase. Clonally sorted EYFP−/EBFP+ dLP-CHO cells stably integrated with a gene circuit encoding one copy of dCas9-VPR gene and flanking selection marker genes in the dLP1-1 site were used for the second BxB1-mediated integration. The free dLP1-2 site was integrated with a gene circuit containing independent TUs that encoded: the 5′ flanking puromycin gene, gRNA10, the light chain and heavy chain genes of anti-hPD1 driven by the same gRNA10 operators, one copy of dCas9-VPR gene, and the 3′ flanking blasticidin gene linked to dCas9-VPR gene by a 2A self-cleavage peptide sequence. Dually integrated cells were selected with four antibiotics and then subjected to pooled cell sorting based on EYFP−/EBFP− signals. b Octet mAb titer quantitation showed differential anti-hPD1 secretion programmed by four distinct configurations of gRNA10 operators: PD1Ab1 (8× BS), PD1Ab2 (8× BS with SI), PD1Ab3 (16× BS), and PD1Ab4 (16× BS with SI) (one-way ANOVA mixed-effects analysis with multiple comparisons corrected by Tukey test; PD1Ab3 and PD1Ab4 vs. PD1Ab1: p = 0.0160 and p < 0.0001, respectively; PD1Ab4 vs. PD1Ab2: p < 0.0001; PD1Ab4 vs. PD1Ab3: p = 0.0009). c Pearson correlation analysis revealed that anti-hPD1 titers strongly correlated with crisprTF promoter strengths (r = 0.99, R2 = 0.99, p = 0.0051). d Schematic diagram of CHO-tumor-T-cell co-culture system to evaluate the functionality of anti-hPD1 and to explore the utility of our crisprTF promoter platform for cellular therapy. dLP-CHO cells engineered with one of the above four configurations for anti-hPD1 secretion were first seeded for 48 hours. The control group was seeded with EYFP−/EBFP+ dLP-CHO cells with no anti-hPD1 payload circuit. Pre-activated human T cells and human ovarian cancer cells (OVCAR8) expressing a surface T-cell engager were subsequently seeded in each well with the attached dLP-CHO cell populations. e Quantification of IFN-γ concentrations in the media at 24 hours post-co-culture by ELISA revealed tunable IFN-γ production by T cells (one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons corrected by Dunnett test; PD1Ab3 and PD1Ab4 vs. No PD1Ab: p = 0.0248 and p = 0.0049, respectively). All data represent the mean ± SD (n ≥ 3) (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). Source data are provided as Source Data files.