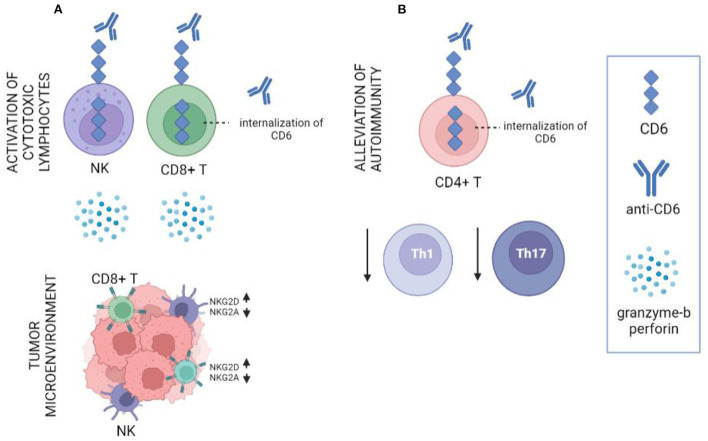
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the role of anti-CD6 (UMCD6) in cancer and autoimmunity. (A) Internalization of CD6 on CD8+ T cells and NK cells with UMCD6 induces the activation of these cells by up-regulation of granzyme-b, perforin and the activating receptors NKG2D, and down-regulation of the inhibitory receptor NKG2A. (B) UMCD6 provides a protective effect in autoimmune diseases by suppression of differentiation of effect Th1 and Th17 cells.