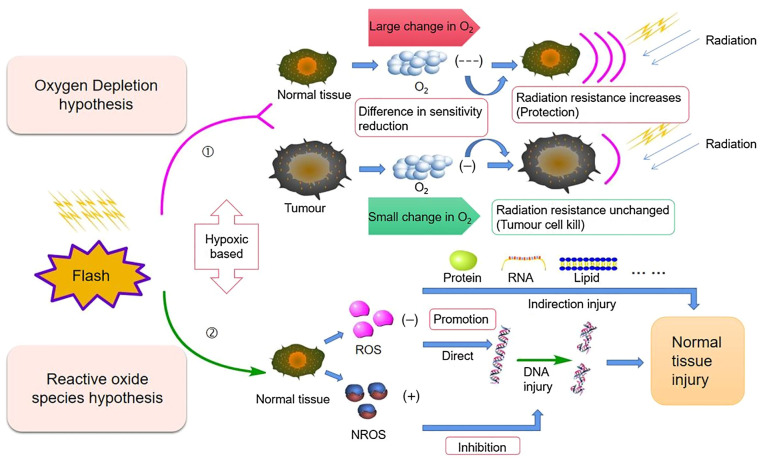
Figure 2.
Mechanistic diagram of the oxygen consumption hypothesis and ROS hypothesis: ①Oxygen consumption hypothesis: High-dose transient irradiation reduces the presence of oxygen, and this effect is greater on normal cells, resulting in stronger radiation resistance; ROS hypothesis: In normal cells in this hypoxic environment, there is a decrease in ②ROS levels that causes DNA, RNA, protein and lipid injury, and an increase in the protective NROS levels that inhibits DNA injury. NROS, non-reactive oxygen species.