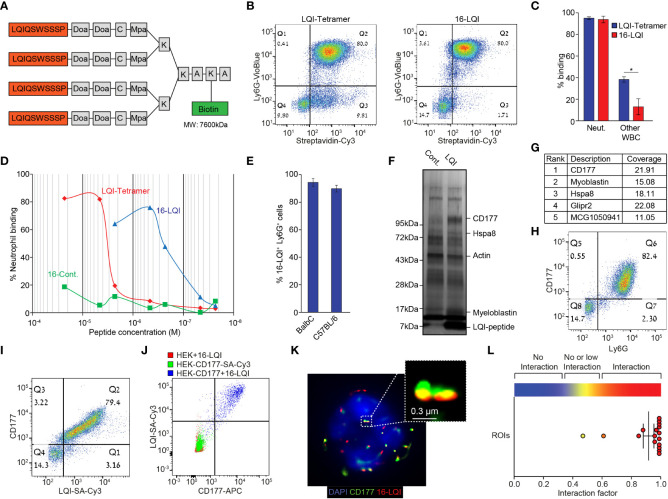
Figure 1.
Murine Neutrophil-Specific LQI-Peptide binding via CD177. (A) Schematic representation of the biotin-LQI-tetramer. (B) FACS analysis comparing the binding of LQI tetramer (left) and 16-LQI (right) to WBC following 20 min. incubation with 1μM of each. (C) Quantification of LQI tetramer (blue) or 16-LQI (red) binding to neutrophils and other WBC. (D) Mouse neutrophils were incubated with the LQI-tetramer, the 16-LQI complex and the 16-Cont. (human neutrophil binding peptide - KFP) complex in increasing concentration. The samples were then analyzed by flow cytometry and the presented shows the fraction of Cy3+ neutrophils (Ly6G+). The 16-LQi and the 16-Cont. were preincubated with SA-Cy3, the LQI-tetramer was first incubated with the cells and then incubated with SA-Cy3. (E) Quantification of FACS analysis of the extent of binding of 16-LQI (1μM) to circulating Ly6G+ neutrophils from healthy Balb/C and C57BL/6 mice (n=3). (F) Silver staining of the gel plotting the proteins pulled down using naked (Cont.) and LQI-tetramer decorated (LQI-peptide) SA agarose beads. (G) Top ranking proteins enriched by LQI-tetramer-SA pull down. (H, I) Representative dot plots of isolated WBC stained with Ly6G and CD177 (H) and CD177 and 1μM LQI-tetramer (I). (J) FACS analysis of 16-LQI binding to control HEK293T cells (Red), SA-Cy3 binding to HEK293T cells overexpressing the murine CD177 protein (Green) and CD177-overexpressing HEK293T cells were incubated with 16-LQI (blue). (K) Representative STORM imaging of a single neutrophil with staining of CD177 (green) and 16-LQI (red), overlay with brightfield (left) or DAPI staining of nucleus (right). (L) Quantification of CD177 and 16-LQI interaction for image depicted in (K) using the ImageJ Interaction Factor plugin (35). Error bars represent ± SEM. * p<0.05.