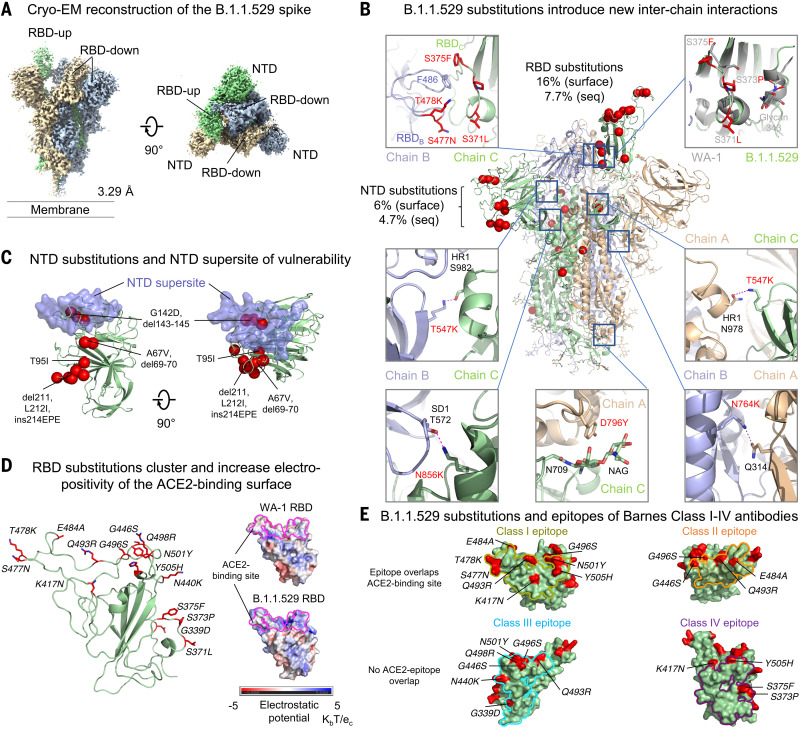
Fig. 1. Cryo-EM structure of the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron) spike.
(A) Cryo-EM map of the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 spike. Reconstruction density map at 3.29 Å resolution is shown with side and top views. Protomers are colored light green, wheat, and light blue. The contour level of cryo-EM map is 4.0σ. (B) B.1.1.529 amino acid substitutions introduced interprotomer interactions. Substitutions in one of the protomers are shown as red spheres. Examples of interprotomer interactions introduced by B.1.1.529 substitutions are highlighted in the box with zoom-in views to the side. Amino acid substitutions are described as a percentage of the domain surface (surface) or as a percentage of the sequence (seq). (C) The NTD supersite of vulnerability is shown in semitransparent surface along with a green backbone ribbon. Amino acid substitutions, deletions, and insertions are in red. (D) The 15 amino acid substitutions, clustered on the rim of RBD, changed 16% of the RBD surface area (left) and increased electropositivity of the ACE2-binding site (right). Amino acid substitutions are shown as red sticks. The ACE2-binding site on the electrostatic potential surface are marked as magenta lines. (E) Mapping B.1.1.529 RBD substitutions on the epitopes of Barnes class I to IV antibodies. The locations of the substitutions are shown in red on the surface. Those that may potentially affect the activity of antibodies in each class are labeled with their residue numbers. Class I footprint is defined by epitopes of CB6 and B1-182.1; class II footprint is defined by epitopes of A19-46.1 and LY-CoV555; class III footprint is defined by epitopes of A19-61.1, COV2-2130, LY-CoV1404 and S309; and class IV footprint is defined by epitopes of DH1047 and S304. Class I and II antibodies primarily target the ACE2 binding site, whereas the epitopes of class III and IV antibodies do not. Class II and III epitopes allow binding to WA-1 when RBD is in the up or down conformation, although the distinction between class I and II is more fluid, particularly with new variants that alter the accessibility of epitopes relative to WA-1. In addition, some antibodies, such as A19-46.1, can bind fully up intermediate states between up and down but cannot bind the fully down state. We therefore classified primarily by binding region.