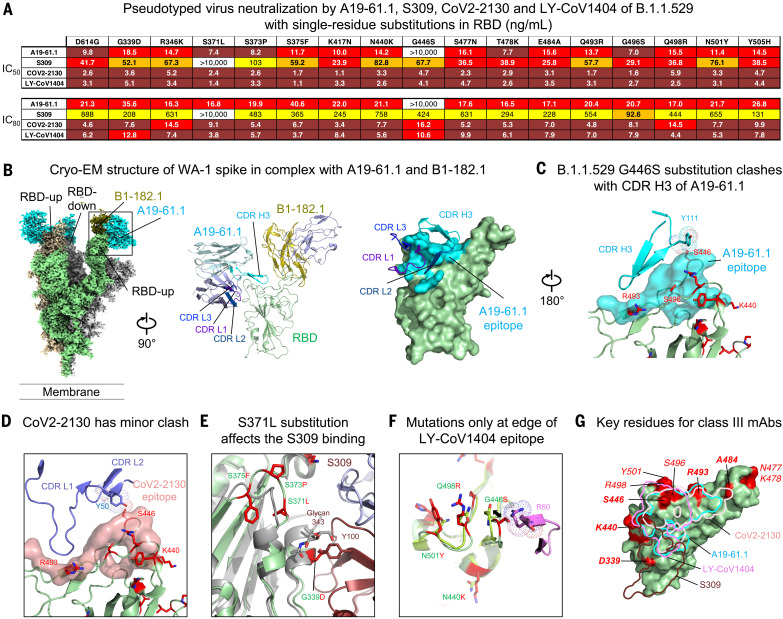
Fig. 5. Functional and structural basis of class III antibody binding, neutralization, and retained potency against the B.1.1.529 VOC.
(A) Lentiviruses pseudotyped with SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins from D614G or D614G plus the indicated point substitutions found within the B.1.1.529 spike were incubated with serial dilutions of the indicated antibodies, and IC50 and IC80 values were determined. A19-61.1 and LY-COV1404 were assayed on 293T-ACE2 cells, whereas S309 and CoV2-2130 were tested on 293 flpin-TMPRSS2-ACE2 cells. Ranges are indicated with white (>10,000 ng/ml), light blue (>1000 to ≤10,000 ng/ml), yellow (>100 to ≤1000 ng/ml), orange (>50 to ≤100 ng/ml), red (>10 to ≤50 ng/ml), maroon (>1 to ≤10 ng/ml), and purple (≤1 ng/ml). (B) Cryo-EM structure of SARS-CoV-2 WA-1 spike in complex with class I antibody B1-182.1 and class III antibody A19-61.1 at 2.83 Å resolution. Overall density map is shown, with protomers in light green, gray, and wheat. Two RBDs are in the up conformation, with each binding both Fabs, and one RBD is in the down position, with A19-61.1 bound. (Left) RBD. B1-182.1 and A19-61.1 are in olive and cyan, respectively. Structure of the RBD with both Fabs bound after local focused refinement is shown to the right in cartoon representation. (Middle) RBD is shown in green cartoon, and antibody light chains are in light blue. (Right) Epitope of A19-61.1 is shown as cyan surface on RBD, with interacting CDRs labeled. The contour level of cryo-EM map is 5.2σ. (C) Structural basis of B.1.1.529 resistance to A19-61.1. Mapping of the A19-61.1 epitope onto the B.1.1.529 RBD indicated that G446S clashed with CDR H3 of A19-61.1. RBD is shown in green cartoon, with amino acid substitutions as red sticks, and epitope of A19-61.1 is the cyan surface. (D) Structural basis of CoV2-2130 neutralization of the B.1.1.529 VOC. Docking of the CoV2-2130 onto the B.1.1.529 RBD showed that Y50 in CDR L2 posed a minor clash with S446. RBD is shown in green cartoon, with amino acid substitutions as red sticks, and epitope of CoV2-2130 is the pink surface. (E) Structural basis of S309 neutralization of the B.1.1.529 VOC. Docked complex of S309 and B.1.1.529 RBD showed that the S371L/S373P/S375F Loop changed conformation, and the S371L substitution is adjacent to the S309 epitope, whereas the G339D substitution is located inside the epitope. D339 side-chain clashes with CDR H3 Y100. B.1.1.529 RBD is shown in green cartoon, with amino acid substitutions as red sticks, and WA-1 RBD is shown in gray cartoon. (F) Structural basis of LY-CoV1404 neutralization of the B.1.1.529 VOC. Docking of the LY-CoV1404 onto the B.1.1.529 RBD identified four amino acid substitutions in the epitope, with G446S causing a potential clash with CDR H2 R60. However, comparison of both LY-CoV1404–bound and –nonbound B.1.1.529 RBD indicated that the S446 loop has the flexibility to allow LY-CoV1404 binding. B.1.1.529 residues at LY-CoV1404 epitope are shown as red sticks, with corresponding WA-1 residues as green sticks. CDR H3 is shown in cartoon representation and colored magenta. (G) Overlay of epitope footprints of class III antibodies onto the B.1.1.529 RBD. Locations of amino acid substitutions in B.1.1.529 RBD are in red on the green surface.