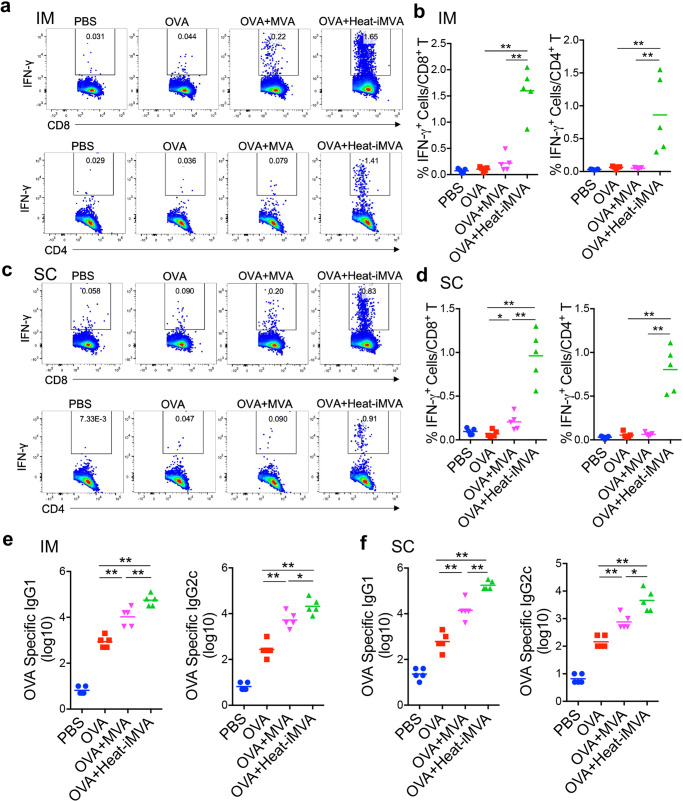
Fig. 1. Co-administration of heat-inactivated MVA (heat-iMVA) enhances antigen-specific T cell and antibody responses after intramuscular (IM) vaccination with chicken ovalbumin (OVA).
WT C57BL/6J mice were vaccinated on day 0 and day 14 with OVA (10 μg), OVA (10 μg) plus MVA (107 pfu) or OVA (10 μg) plus heat-iMVA (an equivalent amount of 107 pfu/mouse) intramuscularly (IM) (a, b, e) or subcutaneously (SC) (c, d, f). On day 21, splenocytes (a–d) were stimulated with OVA257-264 (CD8+ T specific peptide) or OVA323-339 peptide (CD4+ T specific peptide). The expression of IFN-γ by CD8+ T cells or CD4+ T was measured by flow cytometry. e, f OVA-specific immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) or OVA-specific immunoglobulin G2c (IgG2c) titers in the serum from PBS, OVA, OVA + MVA, or OVA + heat-iMVA-vaccinated mice were determined by ELISA. Data are represented as mean ± SEM (n = 3–5; *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01; Two-tailed Mann–Whitney U test). Data are representative of two independent experiments.