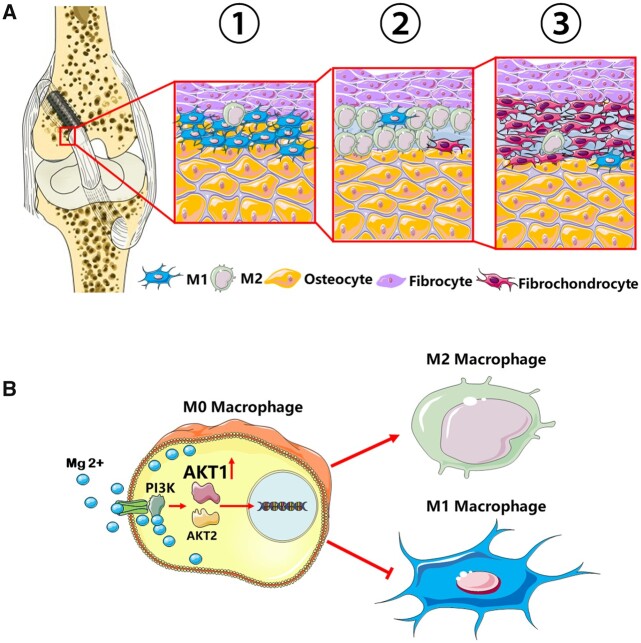
Figure 12.
Schematic diagram showing the mechanism that Mg screws modulated macrophage polarization in the regeneration of fibrocartilaginous entheses during ACL reconstruction via AKT1/AKT2 alternative activation. (A) Tendon graft was fixed by the Mg screws in the femoral tunnel. At the entrance of the femoral tunnel, the surface healing process started with M1 macrophage polarization and accumulation at the tendon–bone interface in the early inflammation phase (Step 1). Macrophages then polarized to M2 type in the reparative phase (Step 2) and promoted the differentiation of BMSCs into fibrochondrocytes at the fibrocartilage interface (Step 3). (B) Implant-derived Mg2+ went through the ion channel and activated the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway. The AKT1, rather than AKT2, was selectively activated and resulted into the polarization of M2 macrophages in the reconstruction of ACL.