Fig. 3.
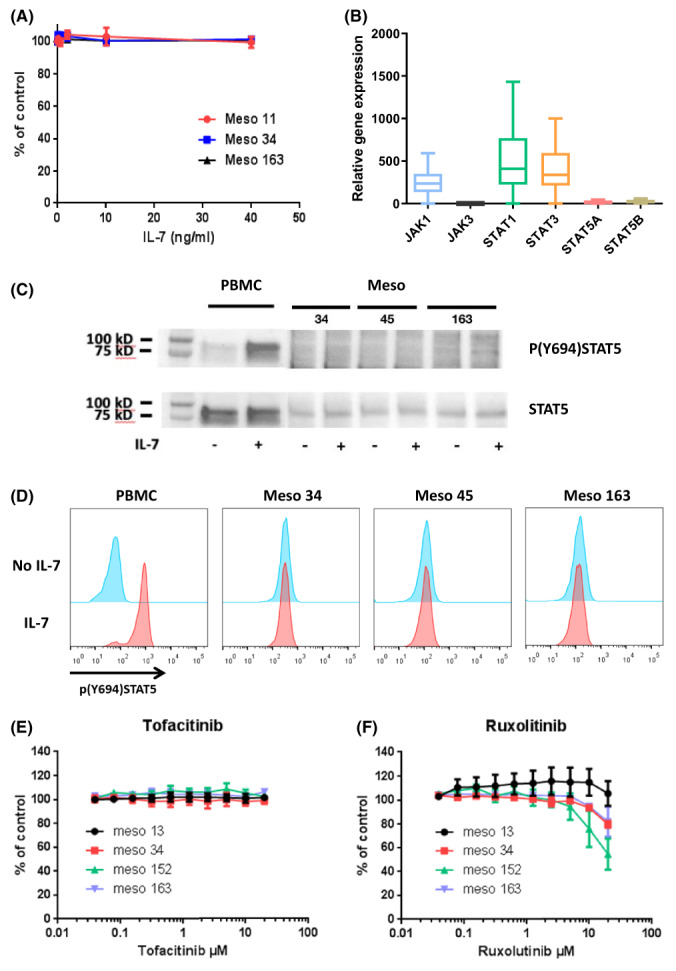
Functional evaluation of the IL‐7R/IL‐7 signaling pathway in MPM. (A) CD127+/CD132+ cells (Meso163), CD127− cells (Meso11), and CD127+/CD132− cells (Meso34) were incubated with increasing doses of IL‐7 for 72 h and cell viability was measured. Results represent means ± SEM of three independent experiments. (B) Expression of genes involved in IL‐7 signaling was measured using RT‐qPCR in MPM cell lines (n = 21). Graphs are whiskers plots (min to max). The line in the middle of the box is plotted at the median. (C, D) CD127+/CD132+ cells (Meso163), CD127+/CD132− cells (Meso45) and CD127+/CD132− cells (Meso34) or PBMC were incubated with IL‐7 for 15 min and then STAT5 phosphorylation was evaluated using western blot (C) or flow cytometry (D). Results are representative of two independent experiments. (E, F) MPM cells were treated with increasing doses of tofacitinib (JAK3i) (E) or ruxolitinib (JAK1/2i) (F) for 72 h and cell viability was measured. Results represent means ± SEM of three independent experiments. MPM, malignant pleural mesothelioma; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
