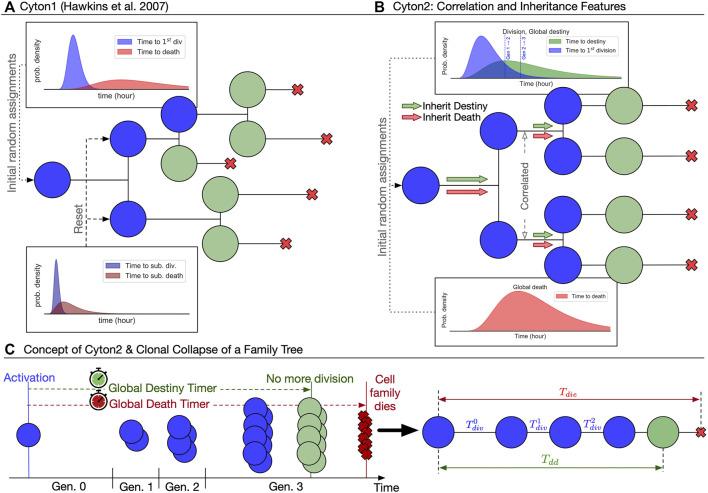
FIGURE 1.
Overview of the two Cyton models. (A) The original Cyton model (Hawkins et al., 2007) where stochastic times to divide and to die are chosen independently after each cell division. Cells cease their motivation to divide based on division-counting mechanism. (B) The Cyton2 model incorporates significant correlation in division times between siblings, as well as familial inheritance of death and division destiny times. (C) A consequence of the correlation and inheritance is that the resulting family trees are heterogeneous, but highly concordant. By exploiting this property, a family tree can be summarised by substituting the average values of its times and fate at each generation. An example of clonally collapsed family tree and its key variables is shown.