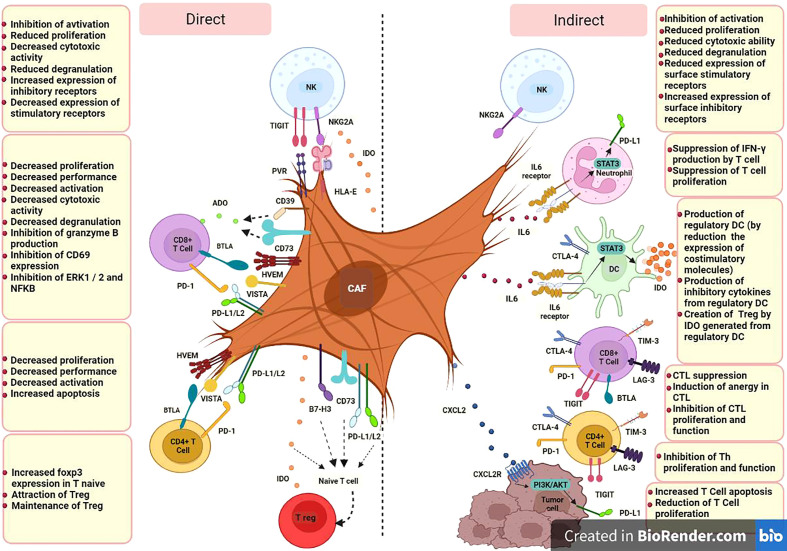
Figure 1.
CAF cells could modulate immune cell function in TME through iICPs in two ways; direct expression of inhibitory membrane-associated molecules and indirect induction of them by producing soluble factors. CD8+ T cell, Cytotoxic T-cell (CTL);CD4+ T cell, Helper T-cell (Th); DC, Dendritic Cell; NK, Natural killer cell; T reg, Regulatory T cell; PD-L1, Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1; PD-L2, Programmed cell death-ligand 2; IDO, Indoleamine 2;3 dioxygenase; ADO, Adenosine; HLA-E, human leukocyte antigen E; PVR, poliovirus receptor; A2B, adenosine A2B receptor; NKG2A, CD159a; TIM-3, T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain containing-3; PD-1, programmed cell death; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen-4; LAG-3, lymphocyte-activation gene- 3; BTLA, B and T lymphocyte attenuator; TIGIT, T cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain; HVEM, herpes virus entry mediator; VISTA, V-domain immunoglobulin suppressor of T cell activation; B7-H3, CD276; CD, Cluster of Differentiation; IL, Interleukin; CXCL, C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand; CXCR, C-X-C chemokine receptor; STAT3, Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; IFN-γ, Interferon-gamma.