Figure 1:
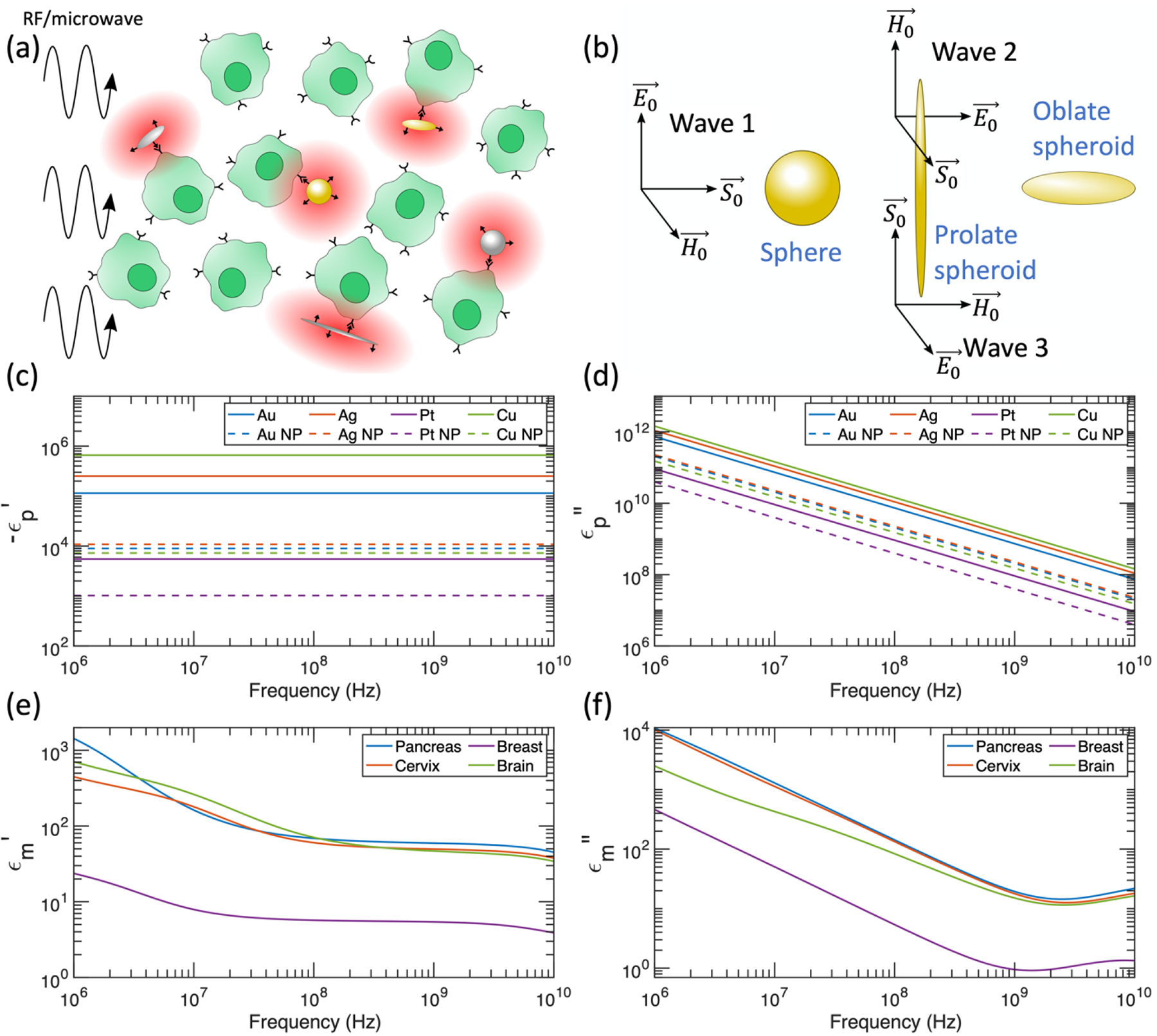
(a) Schematic of differential heating induced by RF/microwave application to cells targeted by metal nanostructures. (b) Orientation of RF/microwave interaction with nanomaterials. The relative absorption ratio is averaged over the 3 propagating waves shown (with equal magnitudes) to account for a collection of randomly oriented spheroids. (c) Negative real component of the dielectric function for metals considered in this manuscript. Dashed curves include scattering rate corrections for spherical nanoparticles with 10 nm radius (NP = nanoparticle). (d) Imaginary component of the dielectric function for metals considered in this manuscript. Dashed curves include scattering rate corrections for spherical nanoparticles with 10 nm radius. (e) Real component of the dielectric function for tissues considered in this manuscript. Data from reference [37]. (f) Imaginary component of the dielectric function for tissues considered in this manuscript. Data from reference [37].
