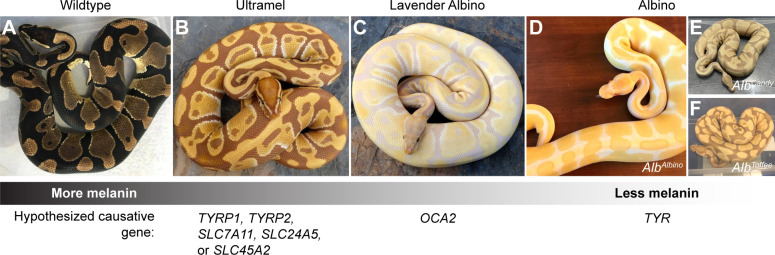
Fig 1. The Albino, Lavender Albino, and Ultramel color morphs have reduced brown-to-black coloration, characteristic of a loss of melanin.
Red-to-yellow coloration is unaffected in these morphs. Hypothesized causative genes represent genes in which loss-of-function variants in other vertebrates produce similar phenotypes (Table 1). (A) Wildtype. (B) Ultramel. (C) Lavender Albino. (D-F) Albino. Phenotypes within the Albino color morph are variable, with some animals having skin patches that are white and others having skin patches that are light beige. (D) Albino animal described as an AlbAlbino homozygote. (E) Albino animal described as an AlbCandy homozygote. (F) Albino animal described as an AlbToffee homozygote. Photo credits, Ryan Young of Molecular Reptile, Chiron Graves, Phil Barclay, Michael Freedman of The Florida Reptile Ranch.